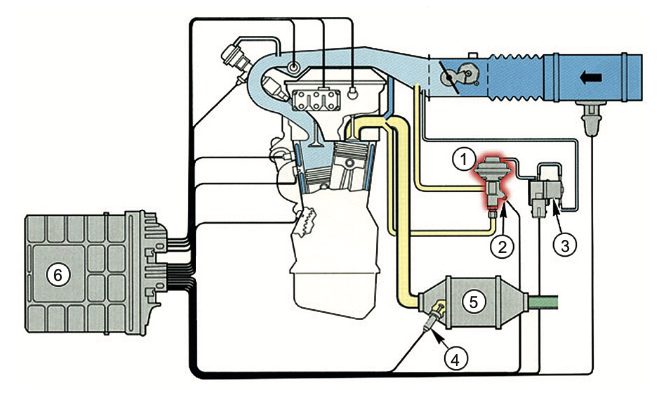
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is a system commonly found in modern vehicles that helps to reduce the amount of nitrogen oxides (NOx) that are produced during combustion. It works by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine’s combustion chamber, where they mix with the incoming air and fuel, and then burn again.
How does the EGR system work?
The EGR system works by diverting a small amount of exhaust gas from the exhaust manifold and routing it back into the engine’s intake system. This exhaust gas is mixed with the incoming air and fuel, which reduces the temperature inside the combustion chamber. The lower temperature helps to reduce the formation of NOx, which is a harmful gas that contributes to smog and other air pollution.
There are several different types of EGR systems that can be found in modern vehicles, including:
- Low-pressure EGR – This system recirculates exhaust gases back into the engine at low pressure, typically just after the turbocharger.
- High-pressure EGR – This system recirculates exhaust gases back into the engine at high pressure, typically just before the intake manifold.
- Exhaust gas cooling – This system cools the exhaust gases before they are recirculated back into the engine, which further reduces the formation of NOx.
- Exhaust gas mixing – This system mixes the recirculated exhaust gases with fresh air before they enter the combustion chamber.
What are the benefits of the EGR system?
The primary benefit of the EGR system is that it helps to reduce the amount of NOx that is produced during combustion. This is important because NOx is a harmful gas that contributes to air pollution, and can also have negative health effects on humans and animals.
In addition to reducing NOx emissions, the EGR system can also help to improve fuel efficiency and reduce engine wear. By reducing the temperature inside the combustion chamber, the EGR system can help to prevent engine knock, which can cause damage to the engine over time. This can help to extend the life of the engine and reduce maintenance costs.
Are there any downsides to the EGR system?
While the EGR system can provide many benefits, there are some downsides to consider. One potential issue is that the recirculated exhaust gas can contain particulate matter, which can build up over time and cause problems with the engine or emissions control system.
Another potential downside is that the EGR system can reduce the power output of the engine, particularly at low speeds or under heavy load. This can result in reduced performance, which may not be desirable for some drivers.
Overall, the EGR system is an important component of modern vehicles that helps to reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency. While there are some potential downsides to consider, the benefits of the system generally outweigh the drawbacks. If you are concerned about the EGR system in your vehicle, it is always best to consult with a qualified mechanic or automotive technician to ensure that your vehicle is running properly and safely.
The EGR system was first introduced in the 1970s as a way to reduce emissions from vehicles. Since then, it has become a standard feature in most modern vehicles, particularly those with diesel engines. The system is required to meet emissions regulations, particularly for nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions, which are regulated by most countries.
NOx is a harmful gas that is formed when nitrogen and oxygen in the air react at high temperatures, such as inside an engine’s combustion chamber. NOx emissions contribute to smog, acid rain, and other air pollution, which can have negative health effects on humans and animals. The EGR system helps to reduce NOx emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine’s combustion chamber, where they are cooled and diluted with fresh air before being burned again.
As mentioned earlier, there are several different types of EGR systems that can be found in modern vehicles. The type of system used will depend on the specific engine design and emissions regulations in the country where the vehicle is sold.
Low-pressure EGR systems are typically found in gasoline engines and some diesel engines, and they recirculate exhaust gases back into the engine at low pressure, typically just after the turbocharger. This type of system can help to reduce NOx emissions, particularly at low engine speeds.
High-pressure EGR systems are typically found in modern diesel engines and recirculate exhaust gases back into the engine at high pressure, typically just before the intake manifold. This type of system can provide greater NOx reduction, particularly at high engine speeds.
Exhaust gas cooling is a type of EGR system that cools the exhaust gases before they are recirculated back into the engine. This can further reduce the temperature inside the combustion chamber and reduce NOx emissions.
Finally, exhaust gas mixing is a type of EGR system that mixes the recirculated exhaust gases with fresh air before they enter the combustion chamber. This can help to improve the combustion process and reduce emissions.
While the EGR system provides many benefits, there are some potential downsides to consider. As mentioned earlier, the recirculated exhaust gas can contain particulate matter, which can build up over time and cause problems with the engine or emissions control system. In addition, the EGR system can reduce the power output of the engine, particularly at low speeds or under heavy load.
To ensure that the EGR system is working properly, most vehicles are equipped with sensors and diagnostic systems that can detect problems with the system. If you suspect that there is an issue with your vehicle’s EGR system, it is always best to consult with a qualified mechanic or automotive technician who can diagnose and repair the problem.
Overall, the EGR system is an important component of modern vehicles that helps to reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency. While there are some potential downsides to consider, the benefits of the system generally outweigh the drawbacks.
Advantages:
- Reduced Emissions: The primary advantage of the EGR system is that it helps to reduce harmful emissions, particularly nitrogen oxides (NOx) that are harmful to the environment and human health.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: EGR can also help to improve fuel efficiency, by recirculating some of the hot exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber to reduce the engine’s workload and improve its efficiency.
- Low Cost: EGR systems are relatively inexpensive to manufacture and install, making them a cost-effective solution for reducing emissions in modern vehicles.
- Enhanced Engine Durability: EGR can also help to reduce the temperature of the engine, which can improve its overall durability and longevity.
Disadvantages:
- Reduced Power Output: EGR systems can reduce the engine’s power output, particularly at low speeds or under heavy load, which can impact the vehicle’s overall performance.
- Increased Complexity: EGR systems add complexity to the engine and may require additional sensors, valves, and control systems, which can increase the risk of malfunctions or failures.
- Increased Maintenance: The EGR system requires periodic maintenance, such as cleaning or replacement of the valves, to ensure that it is functioning properly.
- Potential for Clogging: Recirculated exhaust gases can contain particulate matter that may build up over time and clog the system, leading to poor engine performance or emissions problems.
Overall, the benefits of the EGR system generally outweigh the drawbacks, but it is important to consider the potential disadvantages when assessing the suitability of the system for a particular application.