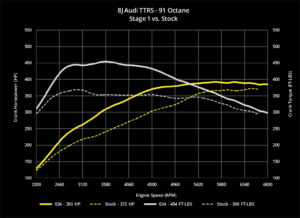
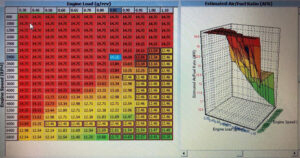
Turbochargers are a key component of modern automotive engineering, allowing engines to generate more power without increasing their size or fuel consumption. In this blog post, we will delve into the science behind turbochargers, how they work, and their benefits.
What is a Turbocharger? A turbocharger is a type of forced induction system that uses exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which in turn drives a compressor. The compressor takes in air from the surrounding environment and compresses it before delivering it to the engine’s intake manifold. This increases the density of air that enters the engine, allowing more fuel to be burned and creating more power.
How does a Turbocharger work? The turbocharger is made up of two main components: a turbine and a compressor. The turbine is located in the exhaust system and is driven by the exhaust gases. As the exhaust gases flow over the turbine blades, they cause the turbine to spin at high speeds, which in turn spins the compressor.
The compressor is located in the air intake system and is responsible for compressing the air that enters the engine. As the compressor spins, it draws in air from the surrounding environment and compresses it before delivering it to the engine’s intake manifold. The compressed air is then mixed with fuel in the combustion chamber and ignited, creating a powerful explosion that generates more power than a naturally aspirated engine.
What are the benefits of a Turbocharger? Turbochargers offer several benefits over naturally aspirated engines. The most significant benefit is increased power output. By compressing the air that enters the engine, turbochargers allow more fuel to be burned, which creates more power. This means that smaller engines can produce the same amount of power as larger engines, which is important for fuel efficiency.
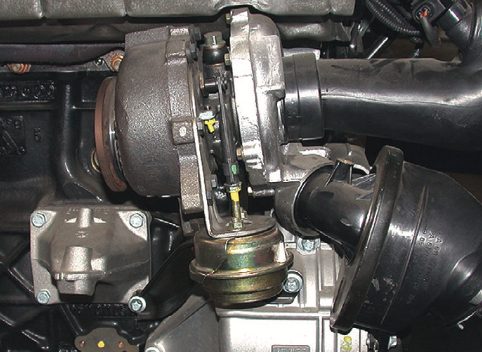
Another benefit of turbochargers is improved efficiency. Since turbochargers use exhaust gases to spin the turbine, they help to extract more energy from the engine’s exhaust system. This means that turbocharged engines can achieve better fuel economy than naturally aspirated engines, even when producing more power.
Finally, turbochargers offer better performance at high altitudes. As air pressure decreases at higher altitudes, naturally aspirated engines struggle to maintain their power output. Turbochargers, on the other hand, are not affected by changes in air pressure, since they compress the air before it enters the engine.
In conclusion, turbochargers are an essential component of modern automotive engineering, allowing engines to generate more power without increasing their size or fuel consumption. By compressing the air that enters the engine, turbochargers offer improved performance, efficiency, and high altitude performance. As engine technology continues to advance, turbochargers will undoubtedly play a vital role in driving the next generation of automotive innovation.
Turbochargers are commonly used in modern engines to increase power output and improve fuel efficiency. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of turbochargers:
Advantages:
- Increased Power Output: Turbochargers can increase the power output of an engine by compressing the incoming air, which allows more air and fuel to be burned per cycle.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Turbochargers can also improve the fuel efficiency of an engine because the engine is able to produce more power without burning more fuel.
- Smaller Engine Size: A turbocharged engine can produce the same power output as a larger naturally aspirated engine, which means that the engine can be smaller and lighter.
- Reduced Emissions: Turbochargers can also help reduce emissions because the engine is burning fuel more efficiently.
Disadvantages:
- Lag: One of the biggest disadvantages of turbochargers is turbo lag. This is the delay between the time when the driver presses the accelerator and the time when the turbocharger starts to spool up and provide boost. This can make the car feel sluggish when accelerating from a stop.
- Heat: Turbochargers generate a lot of heat, which can cause problems if not properly managed. This heat can cause the engine oil to break down and can also cause parts to warp or crack.
- Complexity: Turbochargers are complex systems that require additional components, such as intercoolers and wastegates, to function properly. This complexity can make them more expensive to manufacture and maintain.
- Reliability: Turbochargers can be less reliable than naturally aspirated engines because they have more moving parts and are subjected to higher stresses. They require regular maintenance, such as oil changes and air filter replacements, to prevent premature failure.