In recent years, advances in automotive technology have led to the development of new and improved petrol/gasoline injection systems. These systems play a crucial role in delivering fuel to the engine, and the latest innovations are helping to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance overall engine performance.
One of the most significant developments in petrol/gasoline injection systems is the use of direct injection technology. Unlike traditional port fuel injection, which sprays fuel into the intake manifold and relies on the intake valve to distribute it to the combustion chamber, direct injection delivers fuel directly to the combustion chamber.
This approach allows for more precise fuel metering, which can lead to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Direct injection also allows for higher compression ratios, which can improve engine performance by increasing power and torque output.

Another important innovation in petrol/gasoline injection systems is the use of variable valve timing technology. This technology allows for more precise control over the timing and duration of the intake and exhaust valves, which can improve engine performance and efficiency.
Variable valve timing can also help reduce emissions by allowing the engine to operate more efficiently at different speeds and loads. Some advanced petrol/gasoline injection systems also incorporate variable valve lift technology, which can further enhance engine performance by optimizing the intake and exhaust valve timing and lift for different driving conditions.
Fuel pressure and delivery systems have also seen significant improvements in recent years. High-pressure fuel systems are becoming more common, which can improve fuel atomization and distribution, leading to better engine performance and efficiency.
Some new petrol/gasoline injection systems also incorporate multi-stage fuel injection, which can provide better fuel delivery at high engine speeds and loads. Multi-stage injection systems can also improve cold-start performance and reduce emissions.
In addition to these technical innovations, many new petrol/gasoline injection systems incorporate advanced electronic control systems. These systems can monitor a wide range of engine and vehicle parameters and adjust fuel delivery and timing in real-time to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
Overall, the latest developments in petrol/gasoline injection systems are helping to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance engine performance. As automotive technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovations in this critical component of modern engines.
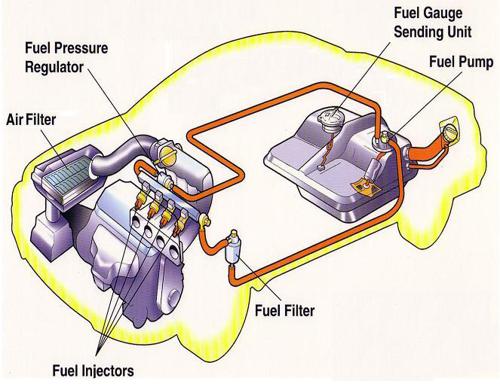
Firstly, it’s important to understand the difference between traditional port fuel injection (PFI) and direct injection (DI). In a PFI system, fuel is injected into the intake manifold just upstream of the intake valve. As the air/fuel mixture flows past the valve, it is drawn into the combustion chamber where it is ignited.
In a DI system, on the other hand, fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber through a high-pressure injector mounted in the cylinder head. This allows for much greater control over the timing, duration, and volume of fuel delivery, which can lead to more efficient combustion and improved performance.
One of the challenges of direct injection is that it can lead to increased carbon buildup on the intake valves, which can affect engine performance over time. To combat this, some manufacturers have developed “dual injection” systems that combine direct injection with traditional PFI. The PFI system is used at low engine speeds and loads to help keep the intake valves clean, while the DI system is used at higher speeds and loads to optimize performance.
Another area of innovation in petrol/gasoline injection systems is the use of multiple injection events. In a traditional PFI system, fuel is typically injected in a single pulse during each engine cycle. But in a multi-stage injection system, fuel is injected in two or more pulses during each cycle.
This allows for more precise control over fuel delivery, which can lead to improved combustion efficiency and reduced emissions. For example, a “split injection” system might inject a smaller initial pulse of fuel to create a leaner air/fuel mixture, followed by a larger second pulse to achieve the desired combustion characteristics.
Along with these technical innovations, there are also several design factors that can affect the performance of petrol/gasoline injection systems. For example, the size and shape of the fuel injector nozzle can have a significant impact on fuel atomization and distribution, as well as the timing and duration of fuel delivery.
Similarly, the design of the intake manifold and combustion chamber can affect the air/fuel mixture characteristics, which can in turn affect combustion efficiency and emissions. And of course, the overall engine design and tuning must be optimized to take full advantage of the capabilities of the fuel injection system.
Overall, the development of new petrol/gasoline injection systems is a complex and constantly evolving field. But by incorporating advanced technologies like direct injection, variable valve timing, and multi-stage fuel delivery, engineers are finding new ways to improve engine efficiency, performance, and emissions.
Advantages:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: New petrol/gasoline injection systems use advanced technologies like direct injection, variable valve timing, and multi-stage fuel delivery to improve fuel efficiency by delivering the precise amount of fuel to the engine at the right time, reducing fuel wastage and increasing the engine’s power output.
- Reduced Emissions: By providing better control over the air/fuel mixture and optimizing combustion efficiency, modern petrol/gasoline injection systems can help reduce emissions of harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter.
- Better Performance: By delivering fuel directly to the combustion chamber, direct injection can improve engine performance by increasing power output and torque, reducing engine knock, and providing more precise control over the air/fuel mixture.
- Cold Start Performance: Advanced injection systems have improved cold-start performance by providing better fuel atomization and distribution at low temperatures, which is crucial for the engine’s longevity.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Modern petrol/gasoline injection systems have advanced diagnostic features that allow mechanics to diagnose and fix problems quickly and efficiently, reducing the downtime and cost of repairs.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: The latest petrol/gasoline injection systems are generally more expensive than traditional carburetors or port fuel injection systems. This cost can increase the overall cost of the vehicle, making it more expensive for consumers.
- Maintenance Complexity: The latest petrol/gasoline injection systems are more complex than older fuel delivery systems, requiring more specialized tools and knowledge to maintain and repair.
- Higher Fuel Pressure: Direct injection systems operate at higher fuel pressures than traditional PFI systems. This can cause issues with fuel system leaks and failures if not maintained and serviced correctly.
- Carbon Buildup: Some direct injection systems can suffer from carbon buildup on the intake valves, which can decrease engine performance over time and require more frequent maintenance.
- Compatibility Issues: New petrol/gasoline injection systems may not be compatible with older engines, which can limit retrofitting options for older vehicles.
In summary, new petrol/gasoline injection systems offer significant advantages in terms of improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and better performance. However, they also come with some disadvantages like higher costs and increased maintenance complexity, which need to be weighed against the benefits.