Heavy cables are an important component in a vehicle’s electrical system, connecting the battery to the rest of the vehicle’s electrical system. They play a critical role in ensuring the proper operation of the vehicle’s electrical components, such as the starter, alternator, lights, and other accessories. In this blog post, we will discuss the importance of heavy cables, their construction, and maintenance.
What are Heavy Cables?
Heavy cables are cables that are designed to carry high current loads over long distances. In a vehicle’s electrical system, they are used to connect the battery to the starter, alternator, and other electrical components. Heavy cables are made up of a bundle of copper wires, which are braided together and coated in a rubber or plastic insulation to protect them from the environment and prevent electrical shorts.
Why are Heavy Cables Important?
Heavy cables play a critical role in a vehicle’s electrical system. They are responsible for delivering the high current required by the starter motor to crank the engine, and they also carry the current generated by the alternator to recharge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical systems. If the cables are damaged or corroded, they can impede the flow of electricity, which can lead to starting problems, charging problems, and other electrical issues.
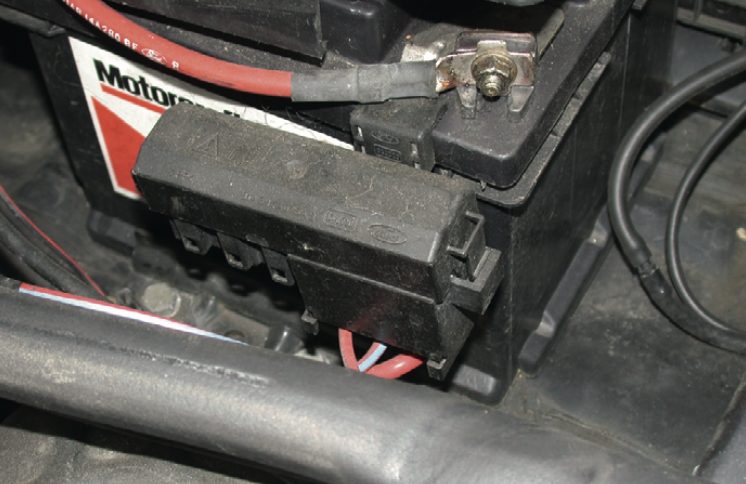

Construction of Heavy Cables
Heavy cables are typically made up of multiple strands of copper wire that are twisted or braided together to form a larger conductor. The more strands the cable has, the more flexible it is, which makes it easier to route through the vehicle’s engine compartment. The copper wires are then coated in a rubber or plastic insulation to protect them from the environment and prevent electrical shorts.
The size of the cable is determined by the amount of current it needs to carry. The larger the current, the larger the cable needs to be. Heavy cables can range in size from 4-gauge to 0-gauge, with 0-gauge being the largest. A larger cable has less resistance and can carry more current without heating up, which is why it is important to use the appropriate size cable for the application.

Maintenance of Heavy Cables
To ensure the proper operation of a vehicle’s electrical system, it is important to maintain the heavy cables. Over time, the cables can become corroded, which can impede the flow of electricity. To prevent corrosion, the cables should be cleaned periodically with a wire brush and a solution of baking soda and water. The connections should also be inspected for tightness and cleaned if necessary.
It is also important to inspect the insulation on the cables. If the insulation is cracked or damaged, it should be replaced to prevent electrical shorts. Any damaged or frayed cables should also be replaced to ensure the proper flow of electricity.
In conclusion, heavy cables are an important component in a vehicle’s electrical system, connecting the battery to the rest of the vehicle’s electrical system. They play a critical role in ensuring the proper operation of the vehicle’s electrical components, such as the starter, alternator, lights, and other accessories. It is important to use the appropriate size cable for the application and to maintain the cables to ensure proper operation.

Heavy cables are critical components of a vehicle’s electrical system as they provide the necessary current to power the starter motor and other electrical components. The starter motor requires a large amount of current to turn the engine over, and if the cables cannot deliver this current, the engine may not start. Similarly, the alternator produces electricity to recharge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical systems. If the cables cannot deliver this current, the battery may not be recharged properly, and the vehicle’s electrical systems may not function correctly.
The construction of heavy cables is an essential factor in their performance. The cables are typically made of multiple strands of copper wire that are twisted or braided together. This design increases the cable’s flexibility, making it easier to route through the engine compartment. The more strands of copper wire a cable has, the more flexible it is. The copper wire is coated with an insulating material, which protects it from the environment and prevents electrical shorts.
The size of a heavy cable is determined by the amount of current it needs to carry. The larger the current, the larger the cable needs to be. The size of a cable is measured by its gauge, which is determined by the diameter of the cable’s conductor. A cable with a larger gauge has a smaller diameter and can carry less current than a cable with a smaller gauge. Therefore, it is essential to choose the appropriate gauge of cable for the application.
One common misconception is that thicker cables always deliver better performance. While thicker cables have less resistance and can carry more current without heating up, using excessively thick cables can actually impede the flow of electricity. This is because the electrical load may not be sufficient to produce the necessary current to flow through the cable, resulting in a drop in voltage. Therefore, it is important to choose the appropriate gauge of cable for the application.
To maintain the proper operation of heavy cables, it is essential to inspect them regularly. Over time, the cables can become corroded, which can impede the flow of electricity. This can be prevented by cleaning the cables periodically with a wire brush and a solution of baking soda and water. The connections should also be inspected for tightness and cleaned if necessary.

In summary, heavy cables are critical components in a vehicle’s electrical system. They provide the necessary current to power the starter motor and other electrical components. The cables are made of multiple strands of copper wire, which are coated with insulating material to protect them from the environment and prevent electrical shorts. The size of a cable is determined by the amount of current it needs to carry, and it is essential to choose the appropriate gauge of cable for the application. Regular inspection and maintenance are required to ensure the proper operation of heavy cables.
Advantages:
- Increased Current Capacity: Heavy cables have a larger diameter and can carry more current than lighter cables. This increased current capacity is essential for powering the starter motor and other high-current devices.
- Reduced Voltage Drop: The thicker the cable, the less resistance it has, and the lower the voltage drop across the cable. This means that devices connected to the cable receive a higher voltage, which can improve their performance.
- Improved Durability: Heavy cables are often more robust and durable than lighter cables, which can be more prone to breakage and wear over time. Heavy cables are less likely to break or become damaged, ensuring reliable operation of the vehicle’s electrical system.
Disadvantages:
- Increased Weight and Bulk: Heavy cables are larger and heavier than lighter cables, which can make them more challenging to install and route in tight spaces. The additional weight can also affect the overall weight and balance of the vehicle.
- Higher Cost: Heavy cables are typically more expensive than lighter cables due to their larger size and increased materials.
- Reduced Flexibility: While heavy cables can be more robust, they are often less flexible than lighter cables. This can make them more difficult to route through the engine compartment, particularly in tight spaces.
Overall, heavy cables provide critical benefits for a vehicle’s electrical system, including increased current capacity, reduced voltage drop, and improved durability. However, they also have some downsides, including increased weight and bulk, higher cost, and reduced flexibility. It is essential to choose the appropriate cable size for the application and ensure that the cables are installed and maintained properly to maximize their performance and reliability.