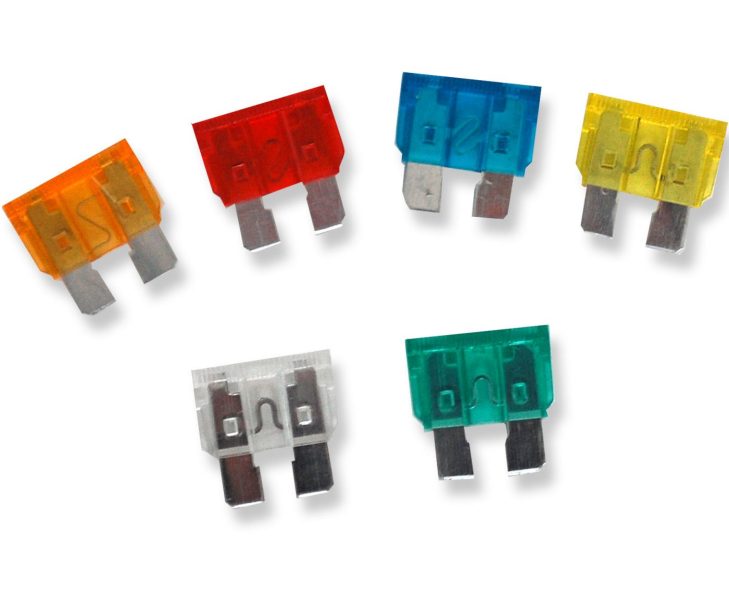
Blade fuses are a type of electrical fuse that is commonly used in automobiles, trucks, boats, and other vehicles. They are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloading, short circuits, and other electrical faults. Blade fuses have become a popular choice for vehicle manufacturers because of their compact size, easy installation, and reliable performance.
In this blog, we will discuss the features, types, and applications of blade fuses.
Features of Blade Fuses:
Blade fuses are small, rectangular fuses that have a plastic body with two metal prongs at each end. The prongs are designed to fit into slots on a fuse holder or a fuse box. The plastic body of a blade fuse is color-coded to indicate its amperage rating. This helps to ensure that the correct fuse is used for a specific application.
Blade fuses are available in different amperage ratings ranging from 1 amp to 40 amps. The amperage rating of a blade fuse indicates the maximum amount of current that it can carry without blowing. The higher the amperage rating, the larger the blade fuse.
Types of Blade Fuses:
There are two main types of blade fuses: standard blade fuses and mini blade fuses.
- Standard Blade Fuses: Standard blade fuses are the most commonly used type of blade fuses. They have a plastic body that measures 19mm x 5mm x 18.5mm and they are available in amperage ratings from 1 amp to 40 amps. Standard blade fuses are used in a wide range of applications including automotive, marine, and industrial applications.
- Mini Blade Fuses: Mini blade fuses are smaller than standard blade fuses and are designed to save space in tight installations. They have a plastic body that measures 10.9mm x 3.6mm x 16.3mm and are available in amperage ratings from 2 amps to 30 amps. Mini blade fuses are commonly used in automotive and marine applications.
Applications of Blade Fuses:
Blade fuses are commonly used in vehicles and other applications that require electrical protection. Some of the most common applications of blade fuses include:
- Automotive Applications: Blade fuses are used in a wide range of automotive applications including the protection of electrical systems such as headlights, taillights, and other vehicle accessories.
- Marine Applications: Blade fuses are commonly used in marine applications to protect electrical systems from saltwater corrosion and other environmental factors.
- Industrial Applications: Blade fuses are used in industrial applications to protect electrical systems in manufacturing, automation, and control systems.
Conclusion:
Blade fuses are an essential component of electrical systems in vehicles, boats, and other applications. They are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloading, short circuits, and other electrical faults. Blade fuses are available in different amperage ratings and types to suit a wide range of applications. Whether you are an automotive mechanic, boat owner, or industrial technician, understanding the features and applications of blade fuses can help you to select the right fuse for your needs.
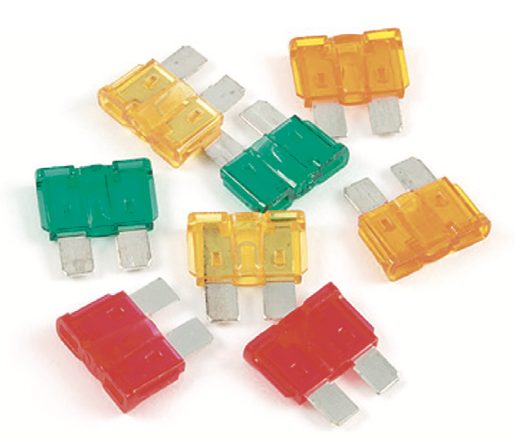

Blade fuses, also known as plug-in fuses, are a type of low voltage fuse that are used in DC (direct current) electrical systems. They are designed to protect the electrical system by breaking the circuit when the current flow exceeds the rated capacity of the fuse.
The plastic body of a blade fuse has a transparent window that allows you to visually inspect the fuse element. When the fuse element melts, it causes the window to turn opaque, indicating that the fuse has blown and needs to be replaced.
In addition to the standard and mini blade fuses, there are also micro blade fuses, which are even smaller than the mini blade fuses, and maxi blade fuses, which are larger than the standard blade fuses. Micro blade fuses are commonly used in modern vehicles, while maxi blade fuses are used in heavy-duty applications such as trucks and buses.
Blade fuses are designed to be easy to install and replace. They simply plug into the fuse holder or fuse box, and can be easily removed by pulling them out with a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers. It is important to use the correct amperage rating for the application to ensure that the electrical system is properly protected.
Blade fuses are widely used in the automotive industry, both in original equipment and aftermarket applications. They are also used in marine, industrial, and recreational vehicle applications. In addition to protecting the electrical system from damage, blade fuses also help to prevent fires caused by electrical faults.
In conclusion, blade fuses are a common and important component of electrical systems in a variety of applications. They provide protection against electrical faults and help to prevent damage to the system and potential safety hazards. By selecting the correct amperage rating and type of blade fuse, you can ensure that your electrical system is properly protected and functioning at its best.
Advantages of Blade Fuses:
- Compact Size: Blade fuses have a small and compact design that saves space and allows for easy installation in tight spaces.
- Easy Replacement: Blade fuses can be easily replaced without the need for any special tools. This makes them a convenient option for DIY enthusiasts and mechanics.
- Color-Coded: Blade fuses are color-coded based on their amperage rating, making it easy to identify and replace the correct fuse.
- Reliable Performance: Blade fuses have a low resistance, which reduces the chance of voltage drops and increases the reliability of the electrical system.
- Cost-Effective: Blade fuses are a cost-effective solution for protecting electrical systems from damage and short circuits.
Disadvantages of Blade Fuses:
- Limited Amperage Range: Blade fuses have a limited amperage range and are not suitable for high current applications.
- Limited Voltage Rating: Blade fuses have a maximum voltage rating of 32 volts DC, which limits their use in high voltage applications.
- Limited Temperature Range: Blade fuses have a limited temperature range and may not perform well in extreme temperatures.
- Limited Shock Resistance: Blade fuses are not as shock-resistant as other types of fuses and may fail if subjected to vibration or shock.
- Difficult to Identify a Blown Fuse: It can be difficult to identify a blown blade fuse as the fuse element may be hidden inside the plastic body. This can make troubleshooting electrical problems more challenging.
Overall, blade fuses are a reliable and cost-effective solution for protecting electrical systems in a variety of applications. However, they do have some limitations and may not be suitable for high current, high voltage, or extreme temperature applications. It is important to select the correct type and amperage rating of blade fuse for your specific application to ensure proper protection and performance.