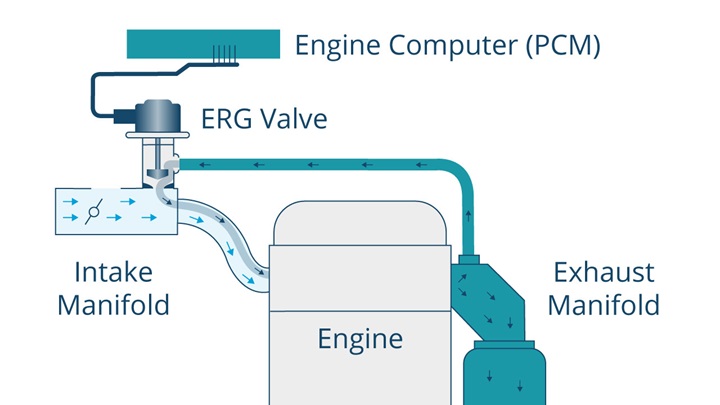
Introduction Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is an emission control technology used in internal combustion engines to reduce the production of nitrogen oxides (NOx). EGR systems work by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the engine’s combustion chamber, diluting the incoming air/fuel mixture and lowering the peak combustion temperature, which reduces the formation of NOx.
In this blog, we will discuss the basics of the EGR system, its working principle, types of EGR systems, and their advantages and disadvantages.
Working Principle of EGR System The EGR system works by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the engine’s combustion chamber. The recirculated exhaust gas consists of unburnt hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides. The recirculation is achieved by a valve, which opens and closes to control the flow of exhaust gas back into the engine’s intake manifold.
The EGR valve is typically controlled by the engine control unit (ECU), which calculates the optimum EGR flow rate based on various engine parameters such as load, speed, and temperature. The EGR valve is usually closed during engine startup and at full load conditions to maintain engine power and efficiency.
Types of EGR Systems There are mainly two types of EGR systems used in internal combustion engines: external EGR and internal EGR.
External EGR: In this type of EGR system, the recirculated exhaust gas is taken from the engine’s exhaust manifold and mixed with the fresh air/fuel mixture before it enters the engine’s combustion chamber. The external EGR system is commonly used in diesel engines.
Internal EGR: In this type of EGR system, the recirculated exhaust gas is taken from the engine’s exhaust port and enters the combustion chamber through the intake valve. The internal EGR system is commonly used in gasoline engines.
Advantages of EGR System The EGR system offers several advantages, including:
- Reduction in NOx emissions: The primary advantage of the EGR system is that it reduces the production of NOx, which is a harmful pollutant.
- Improved fuel efficiency: By reducing the peak combustion temperature, the EGR system can improve the engine’s fuel efficiency by up to 5%.
- Lower combustion noise: The EGR system can also reduce engine combustion noise, making the engine quieter.
Disadvantages of EGR System The EGR system also has some disadvantages, including:
- Reduced engine power: The EGR system can reduce engine power, especially at low speeds, due to the reduced oxygen concentration in the combustion chamber.
- Increased soot buildup: The recirculated exhaust gas can increase the soot buildup in the engine’s intake and exhaust system, leading to increased maintenance costs.
- Reduced engine responsiveness: The EGR system can also reduce engine responsiveness, especially during acceleration, due to the reduced oxygen concentration in the combustion chamber.
Conclusion The EGR system is an essential technology used in internal combustion engines to reduce the production of harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides. The EGR system works by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the engine’s combustion chamber, diluting the incoming air/fuel mixture, and lowering the peak combustion temperature. While the EGR system offers several advantages, it also has some disadvantages, including reduced engine power, increased soot buildup, and reduced engine responsiveness. Nonetheless, the advantages of the EGR system outweigh the disadvantages, making it an important emission control technology in modern engines.
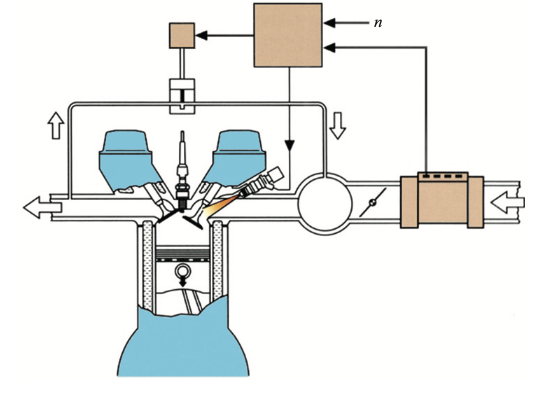
EGR System and Emissions The EGR system plays a crucial role in reducing the engine’s NOx emissions. NOx is a group of harmful pollutants that contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain, and it is also a major contributor to respiratory problems. NOx is produced during the high-temperature combustion of fuel in the engine, and reducing the peak combustion temperature can reduce NOx emissions.
The EGR system works by recirculating some of the exhaust gases back into the engine’s intake manifold or combustion chamber, reducing the concentration of oxygen and increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide and water vapor. This reduces the combustion temperature, which in turn reduces the production of NOx. EGR systems can reduce NOx emissions by up to 70%.
EGR System and Fuel Efficiency The EGR system also has a positive impact on the engine’s fuel efficiency. The recirculation of exhaust gases reduces the oxygen concentration in the combustion chamber, which affects the combustion process. The fuel mixture burns at a lower temperature, which leads to a slower burn rate and a longer combustion duration. This results in better fuel efficiency since more energy is extracted from the fuel.
Additionally, the EGR system can also reduce the engine’s pumping losses. When the engine sucks in air during the intake stroke, it has to overcome the pressure difference between the intake manifold and the outside atmosphere. The EGR system reduces this pressure difference, which reduces the engine’s pumping losses and improves its efficiency.
EGR System and Engine Performance The EGR system can have some impact on the engine’s performance, mainly on its power output and responsiveness. The recirculated exhaust gases reduce the concentration of oxygen in the combustion chamber, which can reduce the engine’s power output, especially at low speeds. This is because the engine needs a higher oxygen concentration to produce more power.
Furthermore, the reduced oxygen concentration can also reduce the engine’s responsiveness, especially during acceleration. The engine needs a higher oxygen concentration to burn more fuel and produce more power, which can cause a delay in the engine’s response.
However, modern engines with advanced EGR systems are designed to minimize these effects on engine performance. The EGR system’s flow rate is controlled by the engine control unit (ECU), which ensures that the recirculation rate is optimal for both emissions and performance.
Types of EGR Systems There are two types of EGR systems: internal EGR and external EGR.
Internal EGR: In internal EGR, the exhaust gas is recirculated through the engine’s combustion chamber. The exhaust gases are mixed with the air/fuel mixture in the intake manifold or enter through the intake valve during the intake stroke.
External EGR: In external EGR, the exhaust gas is recirculated after the exhaust manifold. The exhaust gases are cooled and mixed with the fresh air/fuel mixture before it enters the combustion chamber.
Internal EGR is more commonly used in gasoline engines, while external EGR is more commonly used in diesel engines.
Conclusion The EGR system is an important emission control technology used in modern engines. It plays a critical role in reducing the engine’s NOx emissions and improving its fuel efficiency. While it can have some impact on engine performance, modern engines are designed to minimize these effects. With the increasing focus on reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency, the EGR system is likely to remain a critical component of internal combustion engines in the future.
Sure, here are some advantages and disadvantages of the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system:
Advantages:
- Reduction in NOx emissions: The EGR system can reduce NOx emissions by up to 70%, making it an effective emission control technology.
- Better fuel efficiency: The recirculation of exhaust gases can improve fuel efficiency by reducing the engine’s pumping losses and optimizing the combustion process.
- Cost-effective: The EGR system is a cost-effective way to reduce emissions compared to other emission control technologies.
- Simple design: The EGR system is a simple and reliable system that does not require complex components or maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- Reduced engine performance: The EGR system can reduce engine power output and responsiveness, especially at low speeds, due to the reduced oxygen concentration in the combustion chamber.
- Increased engine complexity: The EGR system adds complexity to the engine, which can increase the risk of failure or malfunction.
- Potential for engine deposits: The recirculation of exhaust gases can lead to the buildup of deposits in the intake manifold and combustion chamber, which can affect engine performance and efficiency.
- Increased exhaust gas temperature: The recirculation of exhaust gases can increase the temperature of the engine’s exhaust gases, which can lead to increased thermal stress on the engine components and potentially reduce the engine’s lifespan.
Overall, while the EGR system has some disadvantages, its advantages in terms of emission reduction and fuel efficiency make it a critical technology for modern engines. Advances in engine design and EGR system technology are continuously improving its effectiveness and reducing its impact on engine performance.