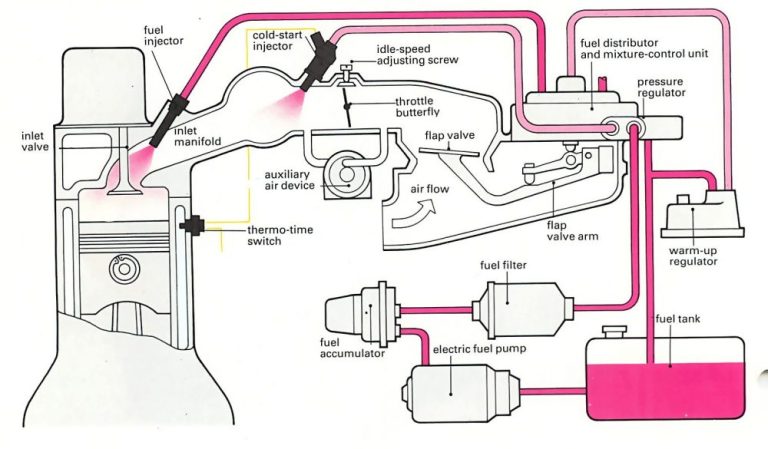
When it comes to powering a vehicle, the ignition and fuel systems play critical roles. The ignition system provides the spark that ignites the fuel in the engine, while the fuel system delivers the necessary fuel to the engine for combustion. In modern vehicles, these two systems are often combined into one system for increased efficiency and performance.
In the past, ignition and fuel systems were separate entities that were responsible for their specific functions. The ignition system was responsible for generating the spark needed to ignite the fuel mixture in the engine, while the fuel system was responsible for delivering the fuel to the engine. These two systems were often independent of each other, and their performance was limited by the technology available at the time.
As technology has advanced, so has the integration of these two systems. Today’s modern vehicles use a combined ignition and fuel system that works together to deliver the best performance and fuel efficiency. This integration has led to improvements in both the ignition and fuel systems, resulting in more efficient and reliable vehicles.
One example of this integration is the use of electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems. EFI systems use electronic sensors to monitor the engine’s conditions and adjust the fuel and ignition systems accordingly. This integration allows for more precise control over the fuel and ignition systems, resulting in improved performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions.
Another example is the use of direct injection systems. Direct injection systems deliver fuel directly to the engine’s cylinders, bypassing the intake manifold. This system provides more precise fuel delivery, resulting in increased power, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. Direct injection systems often use high-pressure fuel pumps that work in conjunction with the ignition system to ensure that the fuel is delivered at the right time and in the right amount.
In addition to increased efficiency and performance, combined ignition and fuel systems have also improved safety. Modern systems are designed to shut off the fuel supply in the event of a crash or other emergency, preventing fuel from igniting and causing a fire.
In conclusion, the integration of ignition and fuel systems has led to significant improvements in vehicle efficiency, performance, and safety. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more advanced systems that will further enhance these benefits. Whether you are driving a modern car or an older model, it is essential to ensure that your ignition and fuel systems are functioning correctly for optimal performance and safety.

One of the primary benefits of integrating the ignition and fuel systems is the ability to adjust and optimize the combustion process for maximum efficiency and performance. The integration allows the systems to work together to achieve the ideal fuel-to-air mixture and timing for combustion. This optimization helps to reduce emissions, increase power, and improve fuel economy.
The combined system also allows for better control and monitoring of the combustion process. Electronic sensors can detect and adjust for changes in air pressure, temperature, and other factors that can affect combustion. The system can adjust the ignition timing, fuel injection timing, and other parameters to ensure the engine is running at peak efficiency.
Electronic control modules (ECMs) are the brains of modern engine management systems. The ECM receives input from various sensors throughout the vehicle and uses that information to control the ignition and fuel systems. The ECM can adjust the fuel-to-air mixture, ignition timing, and other parameters in real-time to optimize engine performance and fuel economy.
Direct injection systems are an example of how the combined ignition and fuel systems have evolved to deliver more power and efficiency. In a direct injection system, fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber, rather than into the intake manifold. This direct delivery allows for a more precise fuel-to-air mixture, resulting in increased power and fuel efficiency.
Another benefit of the combined system is improved safety. Modern systems have safety features that shut off the fuel supply in the event of a crash or other emergency. This safety feature helps to prevent fuel from igniting and causing a fire.
In conclusion, the integration of the ignition and fuel systems in modern vehicles has resulted in significant improvements in efficiency, performance, and safety. The combination of advanced electronic control modules, direct injection systems, and safety features has resulted in vehicles that are more powerful, efficient, and safe than ever before.
Advantages:
- Improved fuel efficiency: Combining the ignition and fuel systems allows for better control and optimization of the combustion process, resulting in increased fuel efficiency.
- Increased power: Modern systems use advanced technologies such as direct injection, which deliver fuel directly to the combustion chamber. This precise delivery results in increased power.
- Better emissions control: Combined systems can adjust fuel-to-air ratios, ignition timing, and other parameters in real-time to optimize combustion, resulting in reduced emissions.
- Enhanced safety: Modern systems have safety features that shut off fuel supply in the event of an emergency, preventing fuel from igniting and causing a fire.
- Improved reliability: Combined systems are more reliable than separate systems since they have fewer parts and are easier to diagnose and repair.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Combined systems are more complex than separate systems, making them more difficult to diagnose and repair.
- Cost: Combined systems are often more expensive to install and maintain than separate systems.
- Reliability: While combined systems are generally more reliable than separate systems, they are still prone to failure and require regular maintenance.
- Compatibility issues: Not all engines are compatible with combined systems, and retrofitting older engines can be difficult and expensive.
- Increased maintenance requirements: Combined systems require regular maintenance to keep them functioning optimally, which can add to the overall cost of ownership.
In conclusion, while the integration of the ignition and fuel systems has resulted in significant improvements in efficiency, performance, and safety, there are also some disadvantages to consider. The complexity, cost, and maintenance requirements of combined systems may not be feasible for all vehicles or users. As with any automotive technology, it’s important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages to determine what is best for your specific needs and situation.