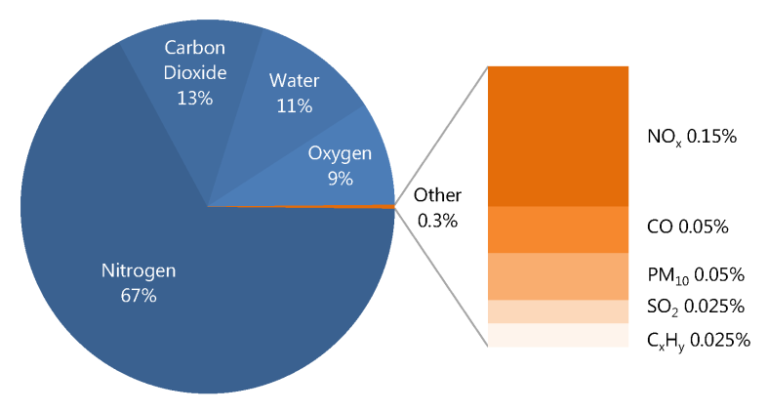
Vehicle exhaust gases are a mixture of several different compounds that are released from the combustion process in the engine. These gases are harmful to the environment and can cause serious health issues if inhaled. Therefore, it is important to understand the approximate composition of vehicle exhaust gases to take steps to reduce their impact on the environment.
The approximate composition of vehicle exhaust gases depends on several factors, including the type of fuel used, engine type, and driving conditions. However, some of the most common gases found in vehicle exhaust include:
- Carbon monoxide (CO): This is a poisonous gas that is formed as a result of incomplete combustion of fuel. It is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, which makes it extremely dangerous. CO is harmful to human health as it binds to hemoglobin in the blood, reducing the amount of oxygen that can be carried to the body’s tissues. This gas is usually produced in higher concentrations in older vehicles.
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx): NOx is a group of gases that includes nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitric oxide (NO). These gases are formed when nitrogen in the air reacts with oxygen during combustion. They are harmful to human health and the environment as they can cause respiratory problems and contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain.
- Hydrocarbons (HC): HC is a group of compounds that are formed when fuel is not completely burned. They are harmful to human health as they can cause respiratory problems and contribute to the formation of smog. HC emissions are usually higher in vehicles with older engines and those that are poorly maintained.
- Particulate matter (PM): PM is a complex mixture of tiny particles that are released from the exhaust system. These particles can cause respiratory problems and contribute to the formation of smog. PM emissions are usually higher in diesel-powered vehicles and those that have been poorly maintained.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): CO2 is a greenhouse gas that is released during the combustion process. It is harmful to the environment as it contributes to global warming.
Reducing vehicle exhaust emissions can be achieved through several measures, including using cleaner fuels, improving engine technology, and implementing better vehicle maintenance practices. Additionally, reducing the number of vehicles on the road and encouraging the use of public transportation and carpooling can also help reduce the impact of vehicle exhaust gases on the environment.
In conclusion, understanding the approximate composition of vehicle exhaust gases is crucial in taking steps to reduce their impact on the environment and human health. The most common gases found in vehicle exhaust include carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, particulate matter, and carbon dioxide. Reducing vehicle emissions can be achieved through several measures, including using cleaner fuels, improving engine technology, and implementing better vehicle maintenance practices.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is formed during incomplete combustion of fuel. It is extremely toxic and can cause serious health issues if inhaled in high concentrations. CO binds to hemoglobin in the blood, reducing the amount of oxygen that can be carried to the body’s tissues. Symptoms of CO poisoning include headaches, nausea, dizziness, and fatigue. Long-term exposure to CO can lead to chronic respiratory problems, heart disease, and neurological damage. In addition to being harmful to human health, CO is also a contributor to air pollution and can cause the formation of smog.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Nitrogen oxides are a group of gases that include nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitric oxide (NO). They are formed when nitrogen in the air reacts with oxygen during combustion. NOx emissions contribute to the formation of smog, acid rain, and respiratory problems. NO2 is particularly harmful to human health and can cause respiratory problems, asthma, and other lung diseases. NOx emissions are regulated by many countries to reduce their impact on the environment and human health.
- Hydrocarbons (HC)
Hydrocarbons are a group of compounds that are formed when fuel is not completely burned. They can be emitted in various forms, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Hydrocarbons can cause respiratory problems and contribute to the formation of smog. Some hydrocarbons are also carcinogenic and can cause cancer with long-term exposure.