Turbochargers have become increasingly popular in the automotive industry due to their ability to increase engine power output and improve fuel efficiency. With the introduction of electronic control systems, turbochargers have become even more efficient and reliable. In this blog, we will discuss the advantages of turbochargers with electronic control and how they work.
Turbocharger Basics
Before we dive into the benefits of electronic control, let’s first go over the basics of a turbocharger. A turbocharger is a forced induction device that uses exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which in turn drives a compressor. The compressor increases the air pressure going into the engine, resulting in more oxygen being available for combustion, which leads to increased power output. Essentially, a turbocharger is like a small windmill that helps the engine breathe better and produce more power.

The Benefits of Electronic Control
While traditional turbochargers rely on exhaust gases to spin the turbine and drive the compressor, electronic control allows for more precise and efficient operation. Here are some of the advantages of turbochargers with electronic control:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency
Electronic control allows the turbocharger to operate more efficiently, which results in improved fuel efficiency. By precisely controlling the amount of air being fed into the engine, the engine can burn fuel more efficiently and produce more power with less fuel. This results in better gas mileage and lower emissions.
- Better Response
Electronic control also allows the turbocharger to respond more quickly to changes in engine load and speed. This means that the engine can produce more power when it’s needed, such as during acceleration or passing, without any lag or delay.
- More Reliable
Electronic control also improves the reliability of the turbocharger. Traditional turbochargers can be prone to failure due to excessive heat or wear and tear. However, electronic control can monitor the turbocharger’s operation and adjust it to prevent damage or failure.
How Electronic Control Works
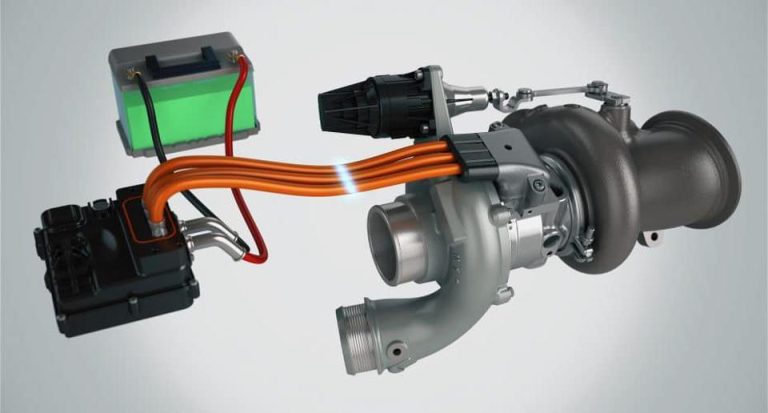
Electronic control of a turbocharger involves using sensors, a control module, and an actuator. The sensors monitor various parameters such as engine load, speed, and temperature. The control module uses this information to determine the optimal amount of air that should be fed into the engine. The actuator then adjusts the turbine’s position to control the air pressure and flow.
Electronic control also allows for variable geometry turbochargers (VGTs). VGTs use adjustable vanes to control the exhaust flow into the turbine, which can adjust the turbocharger’s response and efficiency based on the engine’s needs.
In conclusion, turbochargers with electronic control offer numerous benefits over traditional turbochargers, including improved fuel efficiency, better response, and greater reliability. Electronic control allows for precise monitoring and adjustment of the turbocharger’s operation, resulting in a more efficient and reliable engine. As the automotive industry continues to focus on fuel efficiency and emissions, turbochargers with electronic control will become more common and more advanced.
One of the main advantages of electronic control is the ability to precisely monitor and adjust the turbocharger’s operation. The sensors in the engine can detect various parameters such as engine load, speed, and temperature, which are then used by the control module to determine the optimal amount of air that should be fed into the engine. This information is then used to adjust the position of the turbine and compressor to control the air pressure and flow.
The actuator is a key component of the electronic control system. It is responsible for adjusting the position of the turbine to control the air pressure and flow. There are two main types of actuators: pneumatic and electric.
Pneumatic actuators use compressed air to control the position of the turbine. They are simple and reliable, but they can be slow to respond and may not be as precise as electric actuators.
Electric actuators use an electric motor to control the position of the turbine. They are more precise and responsive than pneumatic actuators, but they can be more complex and expensive.
Variable geometry turbochargers (VGTs) are another innovation made possible by electronic control. VGTs use adjustable vanes to control the exhaust flow into the turbine. This allows the turbocharger to adjust its response and efficiency based on the engine’s needs.
For example, when the engine is operating at low speeds and loads, the VGT can close the vanes to create more back pressure, which helps to spin the turbine faster and produce more boost. At higher speeds and loads, the VGT can open the vanes to reduce back pressure and allow more exhaust gases to flow through the turbine, which helps to maintain boost pressure without overworking the turbocharger.
Electronic control also allows for better monitoring and maintenance of the turbocharger. The control module can detect any issues with the turbocharger’s operation and adjust it to prevent damage or failure. This can help to improve the reliability and longevity of the turbocharger.
In summary, turbochargers with electronic control offer a wide range of benefits over traditional turbochargers. Electronic control allows for precise monitoring and adjustment of the turbocharger’s operation, which results in improved fuel efficiency, better response, and greater reliability. The actuator is a key component of the electronic control system, and there are two main types of actuators: pneumatic and electric. VGTs are another innovation made possible by electronic control, which allows for more precise control of the turbocharger’s response and efficiency.
Advantages of Turbochargers with Electronic Control:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Electronic control allows the turbocharger to operate more efficiently, resulting in improved fuel efficiency. By precisely controlling the amount of air being fed into the engine, the engine can burn fuel more efficiently and produce more power with less fuel.
- Better Response: Electronic control allows for more precise and faster adjustment of the turbocharger, resulting in better engine response. This means that the engine can produce more power when it’s needed, such as during acceleration or passing, without any lag or delay.
- More Reliable: Electronic control can monitor the turbocharger’s operation and adjust it to prevent damage or failure, resulting in greater reliability.
- Variable Geometry Turbochargers: Electronic control allows for the use of variable geometry turbochargers (VGTs), which use adjustable vanes to control the exhaust flow into the turbine. This allows the turbocharger to adjust its response and efficiency based on the engine’s needs, resulting in improved performance and fuel efficiency.
Disadvantages of Turbochargers with Electronic Control:
- Complexity: Electronic control adds complexity to the turbocharger system, which can make it more difficult to diagnose and repair any issues that may arise.
- Cost: Turbochargers with electronic control can be more expensive than traditional turbochargers, which can increase the cost of the vehicle.
- Potential for Electronic Failure: The electronic components of the turbocharger system may be susceptible to failure, which can result in a loss of power or other issues.