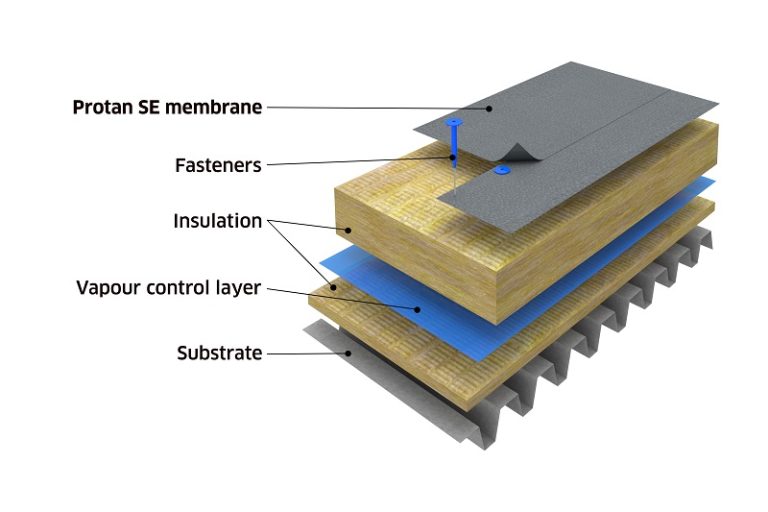
Steel substrate is a material that is commonly used in the construction industry due to its durability and strength. It is made by combining iron and carbon, along with other elements such as manganese, nickel, and chromium. Steel is versatile, and it can be used for a variety of applications, from building structures to manufacturing machinery.
The term “substrate” refers to a surface or material that is coated or bonded with another material. In the case of steel substrate, it is typically coated with a protective layer of another material, such as paint or zinc, to prevent corrosion and increase its longevity.
One of the main advantages of using steel substrate is its strength. Steel is one of the strongest materials used in construction, and it can withstand heavy loads and stress without deformation or failure. This makes it an ideal choice for building structures, bridges, and other infrastructure that must support large amounts of weight.
Another advantage of steel substrate is its durability. Steel is highly resistant to wear and tear, and it can withstand exposure to harsh weather conditions, chemicals, and other environmental factors. This makes it an ideal choice for outdoor applications, such as roofing, siding, and fencing.
In addition to its strength and durability, steel substrate is also highly customizable. It can be cut and shaped to fit specific requirements, and it can be coated with a variety of materials to achieve desired properties, such as improved corrosion resistance or increased friction.
However, steel substrate does have some limitations. One of the main disadvantages is its susceptibility to corrosion. When exposed to moisture and oxygen, steel can rust and corrode, which can weaken its structure and compromise its integrity. To prevent corrosion, steel substrate must be coated with a protective layer, such as paint or zinc.
Another disadvantage of steel substrate is its weight. Steel is a heavy material, which can make it difficult and expensive to transport and install. This is particularly true for large structures, such as bridges or skyscrapers, which require significant amounts of steel.
Overall, steel substrate is a highly versatile and durable material that is widely used in the construction industry. Its strength, durability, and customizability make it an ideal choice for a variety of applications, from building structures to manufacturing machinery. While it does have some limitations, such as its susceptibility to corrosion and its weight, these can be mitigated through proper coatings and design considerations.
As I mentioned earlier, steel substrate is a material that is made by combining iron and carbon, along with other elements such as manganese, nickel, and chromium. The exact composition of steel can vary depending on its intended use and the specific properties that are desired.
One of the main properties of steel that makes it such a popular choice for construction is its strength. Steel is one of the strongest materials used in construction, and it can withstand heavy loads and stress without deformation or failure. This is due to its unique crystalline structure, which consists of tightly packed atoms that are bonded together in a lattice pattern. The strength of steel can be further enhanced through processes such as heat treatment, which can increase its hardness and toughness.
Another property of steel substrate that makes it attractive for construction is its durability. Steel is highly resistant to wear and tear, and it can withstand exposure to harsh weather conditions, chemicals, and other environmental factors. This makes it an ideal choice for outdoor applications, such as roofing, siding, and fencing. However, as I mentioned earlier, steel is susceptible to corrosion, which can weaken its structure and compromise its integrity over time. To prevent corrosion, steel substrate must be coated with a protective layer, such as paint or zinc.
One of the benefits of using steel substrate is its versatility. Steel can be cut and shaped to fit specific requirements, and it can be coated with a variety of materials to achieve desired properties, such as improved corrosion resistance or increased friction. Steel can also be welded, which allows for the creation of complex shapes and structures.
Despite its many advantages, there are some drawbacks to using steel substrate. One of the main disadvantages is its weight. Steel is a dense material, which can make it difficult and expensive to transport and install. This is particularly true for large structures, such as bridges or skyscrapers, which require significant amounts of steel.
Another disadvantage of steel substrate is its cost. Steel is generally more expensive than other construction materials, such as wood or concrete. However, the long-term durability and strength of steel can make it a more cost-effective option in the long run.
In conclusion, steel substrate is a highly versatile and durable material that is widely used in the construction industry. Its strength, durability, and customizability make it an ideal choice for a variety of applications, from building structures to manufacturing machinery. While it does have some limitations, such as its susceptibility to corrosion and its weight, these can be mitigated through proper coatings and design considerations.
Advantages of steel substrate:
- Strength: Steel is one of the strongest construction materials available, and it can withstand heavy loads and stress without deformation or failure.
- Durability: Steel is highly resistant to wear and tear, and it can withstand exposure to harsh weather conditions, chemicals, and other environmental factors.
- Customizability: Steel can be cut and shaped to fit specific requirements, and it can be coated with a variety of materials to achieve desired properties, such as improved corrosion resistance or increased friction.
- Versatility: Steel can be used for a variety of applications, from building structures to manufacturing machinery.
- Sustainability: Steel is a recyclable material, which makes it a more environmentally friendly option than some other construction materials.
Disadvantages of steel substrate:
- Corrosion: Steel is susceptible to corrosion, which can weaken its structure and compromise its integrity over time. To prevent corrosion, steel substrate must be coated with a protective layer, such as paint or zinc.
- Weight: Steel is a dense material, which can make it difficult and expensive to transport and install. This is particularly true for large structures, such as bridges or skyscrapers, which require significant amounts of steel.
- Cost: Steel is generally more expensive than other construction materials, such as wood or concrete.
- Thermal conductivity: Steel is a good conductor of heat and cold, which can make it less energy-efficient than some other materials. This can lead to higher heating and cooling costs for buildings constructed with steel.
- Fire resistance: While steel is fire-resistant, it can lose its strength and integrity when exposed to high temperatures for extended periods of time.
In summary, steel substrate offers many advantages for construction projects, including strength, durability, customizability, versatility, and sustainability. However, it also has some disadvantages, including susceptibility to corrosion, weight, cost, thermal conductivity, and fire resistance. By considering these factors and selecting appropriate coatings and design strategies, construction professionals can effectively leverage the benefits of steel substrate while minimizing its drawbacks.