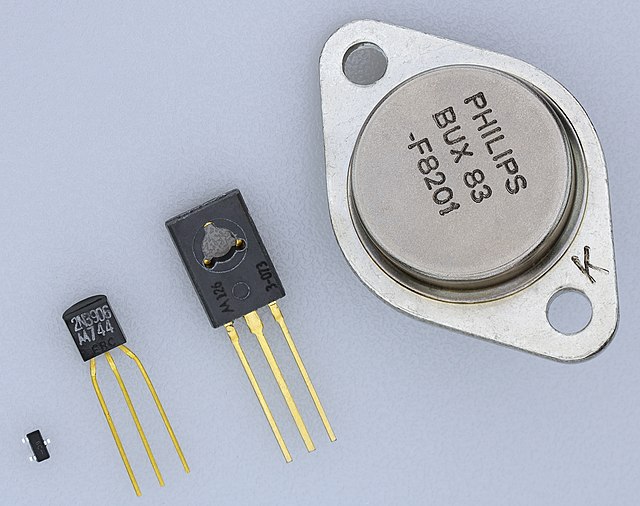
Power transistors are essential components in electronic circuits that provide amplification or switching capabilities. They are designed to handle high voltages and currents, making them ideal for applications that require large amounts of power. In this blog, we will discuss power transistors, their types, and their applications.
What is a Power Transistor?
A power transistor is a type of transistor that is designed to handle high power levels. It is used in electronic circuits to amplify or switch signals. Power transistors are characterized by their high current and voltage ratings, which are typically higher than those of regular transistors.
Types of Power Transistors
There are three main types of power transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJT), metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFET), and insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBT).
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)
BJTs are the oldest and most common type of power transistor. They are made up of three layers of semiconductor material: the emitter, base, and collector. The emitter is doped heavily to produce an excess of electrons, while the base is doped lightly to produce a narrow region that acts as a current control. The collector is doped moderately to produce a reverse-biased junction with the base.
BJTs are available in two types: NPN and PNP. In an NPN transistor, the emitter is made of N-type material, and the collector is made of P-type material. In a PNP transistor, the emitter is made of P-type material, and the collector is made of N-type material.
Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFET)
MOSFETs are a type of transistor that uses a metal gate to control the flow of current. They are made up of a metal gate, an insulating layer, and a semiconductor material. MOSFETs are available in two types: enhancement mode and depletion mode.
In an enhancement mode MOSFET, the channel is not formed until a voltage is applied to the gate. In a depletion mode MOSFET, the channel is already formed, and applying a voltage to the gate reduces the channel conductivity.
Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBT)
IGBTs are a type of transistor that combines the characteristics of both MOSFETs and BJTs. They are made up of a MOSFET and a BJT, and are used in high-power applications such as electric vehicles, power inverters, and motor drives.
Applications of Power Transistors
Power transistors are used in a wide range of electronic applications that require high power levels. Some of the common applications of power transistors include:
- Amplifiers: Power transistors are used in audio amplifiers, RF amplifiers, and other types of amplifiers.
- Switches: Power transistors are used as switches in power supplies, motor drives, and other electronic circuits.
- Voltage regulators: Power transistors are used in voltage regulators to maintain a constant output voltage.
- Power inverters: Power transistors are used in power inverters to convert DC power to AC power.
Conclusion
Power transistors are an essential component in electronic circuits that require high power levels. They are available in different types, including bipolar junction transistors, metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors, and insulated-gate bipolar transistors. Power transistors are used in a wide range of applications, including amplifiers, switches, voltage regulators, and power inverters. When selecting a power transistor for a specific application, it is essential to consider its voltage and current ratings, switching speed, and

How Power Transistors Work
Power transistors are semiconductors that are capable of amplifying or switching signals. They consist of three regions of doped semiconductor material, called the emitter, base, and collector. The emitter and collector are connected to the external circuit, while the base controls the flow of current between the emitter and collector.
When a voltage is applied to the base of the transistor, it allows current to flow between the emitter and collector. This allows the transistor to act as a switch, turning the current on or off in the external circuit. When used as an amplifier, the small input signal is used to control a larger output signal.
Types of Power Transistors
As mentioned earlier, there are three main types of power transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJT), metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFET), and insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBT).
BJTs are the oldest and most common type of power transistor. They are available in two types: NPN and PNP. NPN transistors have an N-type emitter and collector, with a P-type base. PNP transistors have a P-type emitter and collector, with an N-type base. BJT transistors are suitable for applications that require fast switching speeds and high gain.
MOSFETs are transistors that use an electric field to control the flow of current. They are available in two types: enhancement mode and depletion mode. Enhancement mode MOSFETs are normally off, and require a positive voltage on the gate to turn on. Depletion mode MOSFETs are normally on, and require a negative voltage on the gate to turn off. MOSFETs are suitable for applications that require high input impedance and low power dissipation.
IGBTs are transistors that combine the characteristics of both BJTs and MOSFETs. They consist of a MOSFET and a BJT, and are suitable for applications that require high voltage and current handling capability.
Applications of Power Transistors
Power transistors are used in a wide range of electronic applications that require high power levels. Some common applications of power transistors include:
- Audio amplifiers: Power transistors are used in audio amplifiers to provide high power output to speakers.
- Motor drives: Power transistors are used in motor drives to control the speed and direction of motors.
- Power supplies: Power transistors are used in power supplies to regulate the voltage and current output.
- Switching regulators: Power transistors are used in switching regulators to provide efficient power conversion.
- Power inverters: Power transistors are used in power inverters to convert DC power to AC power.
Conclusion
Power transistors are essential components in electronic circuits that require high power levels. They are available in different types, including bipolar junction transistors, metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors, and insulated-gate bipolar transistors. Power transistors are used in a wide range of applications, including amplifiers, switches, voltage regulators, and power inverters. When selecting a power transistor for a specific application, it is important to consider its voltage and current ratings, switching speed, and other characteristics.
Advantages:
- High Power Handling Capability: Power transistors are designed to handle high power levels, making them ideal for applications that require high current and voltage levels.
- Efficient Power Conversion: Power transistors are capable of switching on and off quickly, which makes them suitable for use in switching regulators and power inverters. This results in efficient power conversion with minimal power loss.
- Wide Range of Applications: Power transistors are used in a wide range of applications, including audio amplifiers, motor drives, power supplies, and power inverters.
- Small Size: Power transistors are available in small packages, which makes them suitable for use in compact electronic devices.
Disadvantages:
- Heat Dissipation: Power transistors generate a lot of heat when handling high power levels, which can cause them to overheat if not properly cooled. This can result in reduced reliability and lifespan of the transistor.
- Complex Design: Power transistors are complex devices that require careful design and implementation to ensure proper operation. This can make them difficult to work with for novice electronics enthusiasts.
- Voltage and Current Limitations: Power transistors have voltage and current limitations that must be considered when selecting them for a particular application. Choosing a power transistor that is not rated for the required voltage or current level can result in failure or damage to the device.
- Cost: Power transistors can be expensive compared to other types of transistors, which can make them less attractive for cost-sensitive applications.
In summary, power transistors are capable of handling high power levels and are used in a wide range of applications. However, they can be complex to design and implement, require careful consideration of voltage and current limitations, generate heat that must be dissipated, and can be expensive compared to other types of transistors.