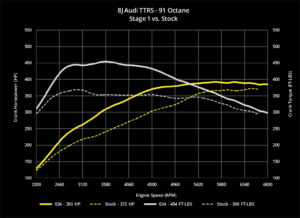
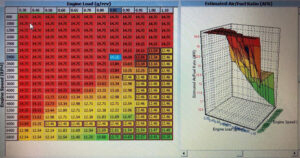
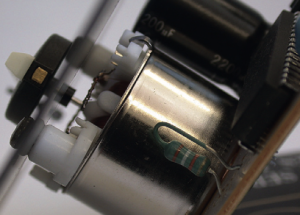
Motor-driven fans are a crucial component in many applications, ranging from HVAC systems to industrial equipment. These fans use an electric motor to power a rotating blade, which generates airflow to circulate air in a room or cool down machinery. In this blog post, we will dive into the specifics of motor-driven fans and explore their design, function, and common applications.
Design of Motor-driven Fans Motor-driven fans consist of two main components: the motor and the blade. The motor provides the power necessary to rotate the blade, while the blade generates airflow by moving the air in a specific direction. The blade can be made from various materials, including plastic, aluminum, and steel. The shape and size of the blade are carefully designed to optimize airflow for the specific application.
The motor of a motor-driven fan can be an AC or DC motor. AC motors are commonly used in HVAC systems, while DC motors are used in industrial equipment and portable fans. The motor is typically housed in a protective casing to prevent damage from the environment, and it may be equipped with a speed control system to adjust the fan’s output.
Function of Motor-driven Fans Motor-driven fans work by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, which is then used to rotate the blade. The blade generates airflow by pushing air in a specific direction, creating a circulation pattern in the room or machinery. The direction of airflow can be adjusted by changing the angle or rotation of the blade.
The airflow generated by a motor-driven fan has several benefits. In HVAC systems, it can help circulate air to remove hot or cold spots and maintain a consistent temperature throughout a building. In industrial equipment, it can help cool down machinery and prevent overheating.
Common Applications of Motor-driven Fans Motor-driven fans are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- HVAC Systems: Motor-driven fans are commonly used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to circulate air and maintain a comfortable temperature.
- Industrial Equipment: Motor-driven fans are used in industrial equipment, such as compressors and generators, to cool down machinery and prevent overheating.
- Electronics: Motor-driven fans are used in electronic devices, such as computers and servers, to remove heat generated by the components and prevent damage.
- Automotive: Motor-driven fans are used in vehicles, such as cars and trucks, to cool down the engine and prevent overheating.
Conclusion Motor-driven fans are a critical component in many applications, ranging from HVAC systems to industrial equipment. They work by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to generate airflow and circulate air. The design and function of motor-driven fans are carefully optimized to provide the best performance for the specific application. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further improvements in the efficiency and performance of motor-driven fans.

One of the key features of motor-driven fans is their ability to be customized for specific applications. As mentioned earlier, the shape and size of the blade can be carefully designed to optimize airflow for the specific application. The motor can also be selected based on the required speed, torque, and power output. Additionally, the casing of the motor-driven fan can be designed to meet specific environmental requirements, such as resistance to dust, moisture, or corrosive chemicals.
Another important factor in the performance of motor-driven fans is the speed at which the blade rotates. The speed can be adjusted using various methods, such as changing the voltage or current supplied to the motor, or using a speed control system. The speed of the fan can be critical for applications such as HVAC systems, where maintaining a consistent temperature and airflow is important.
In addition to their performance features, motor-driven fans can also be designed with safety features to prevent damage or injury. For example, some fans may be equipped with guards to prevent accidental contact with the blades, or thermal switches to prevent overheating.
One area of recent development in motor-driven fans is in the use of smart technology. Smart fans can be connected to a network and controlled remotely using a mobile device or computer. This allows for more precise control of the fan’s output and can provide real-time monitoring of performance and energy consumption.
Overall, motor-driven fans are a versatile and essential component in many industries. Their ability to generate airflow and circulate air is critical for maintaining comfortable environments and preventing damage from overheating. With advancements in technology, we can expect to see further improvements in the performance, efficiency, and safety features of motor-driven fans.
Advantages of Motor-driven Fans:
- Efficient: Motor-driven fans are highly efficient and consume less energy compared to other types of fans. This makes them a cost-effective option for applications that require continuous use.
- Customizable: Motor-driven fans can be customized to meet the specific requirements of a particular application. This includes the size, shape, speed, and motor type, which can be optimized for maximum performance.
- Durable: Motor-driven fans are typically designed with durable materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them suitable for use in industrial settings.
- Easy to Control: The speed of motor-driven fans can be easily controlled using various methods, such as a speed controller or a variable frequency drive. This allows for precise control of airflow and temperature.
- Versatile: Motor-driven fans can be used in a wide range of applications, from HVAC systems to electronic cooling, to automotive engine cooling.
Disadvantages of Motor-driven Fans:
- Noise: Motor-driven fans can produce a significant amount of noise, especially at high speeds. This can be a problem in some applications, such as in residential settings, where noise levels need to be kept to a minimum.
- Maintenance: Motor-driven fans require periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance and prevent breakdowns. This can include cleaning the blades, lubricating the motor, and replacing worn-out components.
- Power Requirements: Motor-driven fans require a source of electricity to operate, which can be a problem in areas with limited power supply or where power outages are common.
- Initial Cost: Motor-driven fans can be more expensive than other types of fans, especially if they are customized for a particular application.
- Safety: The rotating blades of motor-driven fans can pose a safety hazard if not properly guarded or if the fan is not used correctly.
In conclusion, while motor-driven fans offer numerous advantages, they also have some drawbacks that need to be considered when selecting a fan for a particular application. Ultimately, the choice of fan will depend on the specific requirements of the application, such as the required airflow, noise levels, and environmental conditions.