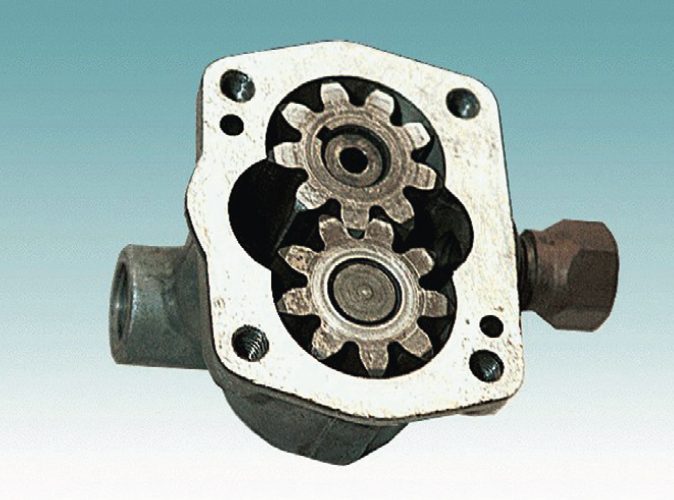
Gear pumps are positive displacement pumps that use two or more gears to transfer fluids or gases from one location to another. They are widely used in many different industries, including automotive, chemical, and pharmaceutical, and they are known for their simple design, durability, and reliable performance.
How Gear Pumps Work
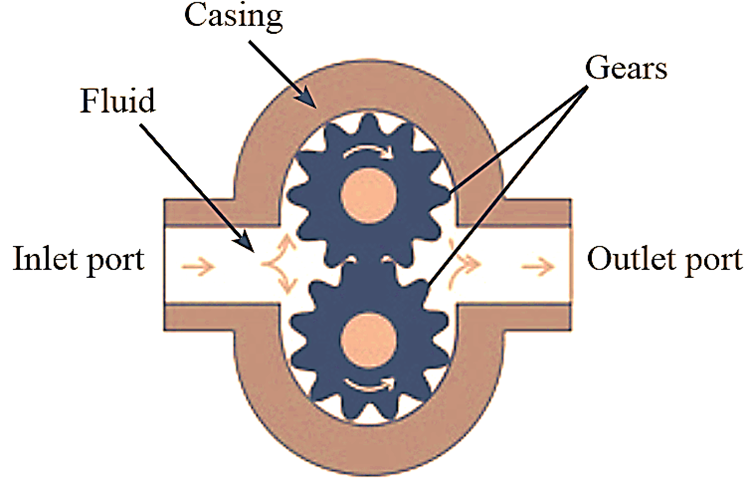
Gear pumps work by using two or more gears that mesh together and rotate inside a casing. One of the gears is connected to a drive shaft, which is typically powered by an electric motor, and the other gear is driven by the first gear. As the gears rotate, they create a vacuum on the inlet side of the pump, which draws fluid or gas into the pump. As the gears continue to rotate, they trap the fluid or gas between the teeth of the gears and the casing, and then force it out through the outlet port.
Types of Gear Pumps
There are two main types of gear pumps: external gear pumps and internal gear pumps.
External gear pumps have two gears that rotate outside the casing. They are relatively simple in design and are typically used for low- to medium-pressure applications.
Internal gear pumps have an internal gear that rotates inside a larger external gear. They are more complex in design but can handle higher pressures and higher volumes of fluid or gas.
Advantages of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps offer several advantages over other types of pumps. Some of these advantages include:
- Simple design: Gear pumps have a relatively simple design that makes them easy to install, operate, and maintain.
- High efficiency: Gear pumps are known for their high efficiency, which means they require less power to operate and can save energy and reduce operating costs.
- Reliable performance: Gear pumps are very reliable and can operate continuously without experiencing significant wear or damage.
- Wide range of applications: Gear pumps can be used to transfer a wide range of fluids and gases, including viscous liquids, corrosive chemicals, and abrasive materials.
Applications of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Automotive: Gear pumps are used in automotive applications, such as oil pumps, fuel pumps, and power steering pumps.
- Chemical: Gear pumps are used in the chemical industry to transfer a variety of chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents.
- Food and Beverage: Gear pumps are used in the food and beverage industry to transfer viscous fluids, such as honey, syrup, and chocolate.
- Pharmaceutical: Gear pumps are used in the pharmaceutical industry to transfer drugs, vaccines, and other medical products.
- Oil and Gas: Gear pumps are used in the oil and gas industry to transfer crude oil, natural gas, and other fluids.
Conclusion
Gear pumps are a reliable and efficient way to transfer fluids and gases from one location to another. They are widely used in many different industries and offer several advantages over other types of pumps, including a simple design, high efficiency, and reliable performance. If you are in the market for a pump, consider a gear pump for your application.

Sure! Gear pumps are a type of positive displacement pump, which means that they transfer fluids by trapping them between moving parts and then forcing them out of the pump. This is different from other types of pumps, such as centrifugal pumps, which use impellers to create a flow of fluid.
Gear pumps can be designed with different types of gears, including spur gears, helical gears, and herringbone gears. Spur gears are the simplest type of gear and are often used in low-pressure applications. Helical gears have angled teeth and can handle higher pressures than spur gears. Herringbone gears are similar to helical gears but have a “V” shape, which makes them even more efficient at handling high pressures.
External gear pumps are commonly used for low- to medium-pressure applications, such as lubrication systems, fuel transfer, and hydraulic systems. They can be designed with different types of materials, such as cast iron, stainless steel, or plastic, depending on the application and the fluid being transferred.
Internal gear pumps are more complex in design and are often used for high-pressure applications, such as in the oil and gas industry. They are known for their ability to handle high volumes of fluid and can be designed with multiple stages to increase the pressure even further.
One of the advantages of gear pumps is their ability to handle viscous fluids, such as oils and syrups. They can also handle fluids with high solids content or abrasive particles, such as in the mining industry. Additionally, gear pumps are often used in metering applications, where precise amounts of fluid need to be transferred.
In summary, gear pumps are a versatile and reliable type of pump that can handle a wide range of fluids and gases. They are widely used in many different industries and offer several advantages, including a simple design, high efficiency, and reliable performance.