Gasoline direct injection (GDI) is a modern engine technology that has become increasingly popular in recent years. GDI has revolutionized the way gasoline engines work by improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. In this blog, we will take a closer look at GDI and how it works.
What is Gasoline Direct Injection?
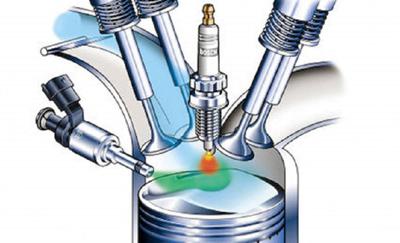
Gasoline direct injection is a fuel injection technology used in gasoline engines. It is a direct injection process in which fuel is directly injected into the combustion chamber of the engine. Unlike traditional fuel injection systems, which spray fuel into the intake manifold, GDI sprays fuel directly into the combustion chamber.
How Does Gasoline Direct Injection Work?
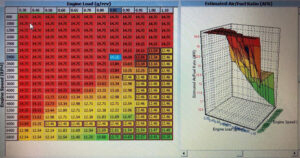
In a GDI system, a high-pressure fuel pump delivers fuel to the injectors. The injectors are located in the combustion chamber and deliver the fuel at high pressure directly into the combustion chamber. The fuel is delivered in a fine mist that mixes with the air in the chamber. This creates a more efficient and complete combustion process, which improves fuel efficiency and reduces emissions.
Benefits of Gasoline Direct Injection
GDI has several benefits over traditional fuel injection systems. First, it improves fuel efficiency by delivering fuel directly into the combustion chamber, which allows for a more precise fuel-air mixture. This results in a more efficient combustion process, which means that less fuel is wasted. GDI engines are also able to operate at higher compression ratios, which further improves fuel efficiency.
Second, GDI reduces emissions by improving the combustion process. Because the fuel is delivered directly into the combustion chamber, there is less fuel wasted and fewer unburned hydrocarbons released into the atmosphere. GDI engines also produce lower levels of carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, which are harmful pollutants.
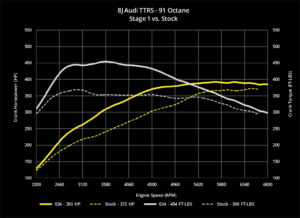
Finally, GDI provides improved performance. Because GDI engines can operate at higher compression ratios, they are able to generate more power and torque than traditional engines. They also provide more precise control over the fuel delivery, which results in more consistent engine performance.
Drawbacks of Gasoline Direct Injection
While GDI provides many benefits, there are also some drawbacks to consider. One of the main drawbacks is that GDI engines can be more expensive to produce than traditional engines. The high-pressure fuel pump, injectors, and other components required for GDI add to the cost of the engine.
Another potential drawback is that GDI engines can be more sensitive to the quality of fuel used. GDI engines require high-quality fuel with a high octane rating to operate effectively. Lower-quality fuels can cause engine damage and reduce performance.
Conclusion
Gasoline direct injection is a modern engine technology that provides many benefits over traditional fuel injection systems. GDI improves fuel efficiency, reduces emissions, and provides improved performance. While there are some drawbacks to consider, GDI is quickly becoming the standard for gasoline engines due to its many benefits. As GDI technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more improvements in the future.
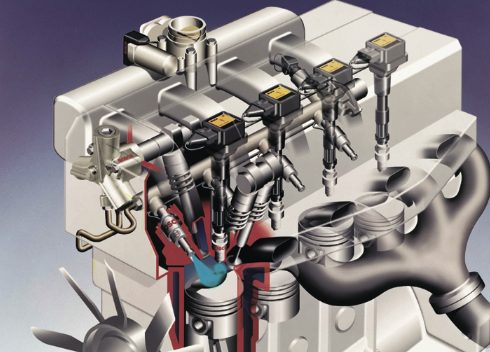
GDI is a fuel delivery system that has been used in diesel engines for many years. However, it was not until the 1990s that GDI was introduced to gasoline engines. Since then, GDI has become increasingly popular as a way to improve the efficiency and performance of gasoline engines.
One of the key advantages of GDI is that it allows for a more precise control over the fuel delivery. Traditional fuel injection systems deliver fuel to the intake manifold, where it mixes with the air before entering the combustion chamber. This can lead to a less efficient combustion process because the fuel is not evenly distributed throughout the combustion chamber.
With GDI, fuel is delivered directly into the combustion chamber at high pressure. This results in a more precise fuel-air mixture, which leads to a more efficient combustion process. The more efficient combustion process means that less fuel is wasted and fewer emissions are produced.
GDI engines also operate at higher compression ratios than traditional engines. This is possible because the fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber, which allows for more precise control over the combustion process. The higher compression ratio means that more power can be generated from the same amount of fuel, which results in improved performance.
However, there are some drawbacks to GDI engines as well. One of the main drawbacks is that they can be more expensive to produce than traditional engines. This is because GDI engines require additional components, such as a high-pressure fuel pump and injectors.
Another potential drawback is that GDI engines can be more sensitive to the quality of fuel used. GDI engines require high-quality fuel with a high octane rating to operate effectively. Lower-quality fuels can cause engine damage and reduce performance.
Despite these drawbacks, GDI is becoming increasingly popular as a way to improve the efficiency and performance of gasoline engines. As GDI technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more improvements in the future.
Sure, here are some advantages and disadvantages of gasoline direct injection:
Advantages:
- Improved fuel efficiency: GDI engines can deliver better fuel efficiency than traditional engines because the fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber, leading to a more precise fuel-air mixture and more efficient combustion.
- Reduced emissions: GDI engines produce fewer emissions than traditional engines because the more efficient combustion process results in less fuel waste and fewer unburned hydrocarbons released into the atmosphere.
- Improved performance: GDI engines can generate more power and torque than traditional engines because they can operate at higher compression ratios, providing more precise control over the fuel delivery and resulting in more consistent engine performance.
- Less carbon buildup: GDI engines are less prone to carbon buildup because the fuel is delivered directly into the combustion chamber, preventing the fuel from contacting the intake valves.
- Better cold-start performance: GDI engines start more easily in cold weather because the fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber, reducing the amount of time it takes for the engine to warm up.
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost: GDI engines can be more expensive to produce than traditional engines because they require additional components, such as a high-pressure fuel pump and injectors.
- Sensitive to fuel quality: GDI engines require high-quality fuel with a high octane rating to operate effectively. Lower-quality fuels can cause engine damage and reduce performance.
- Higher maintenance requirements: GDI engines require more maintenance than traditional engines because the high-pressure fuel system and injectors can become clogged over time, leading to decreased engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Increased engine noise: GDI engines can be noisier than traditional engines because of the high-pressure fuel injection system.
- Potential for carbon buildup on injectors: GDI engines are prone to carbon buildup on the fuel injectors, which can cause decreased engine performance and fuel efficiency over time. Regular cleaning of the injectors is necessary to prevent this buildup.
Overall, GDI technology offers several advantages over traditional fuel injection systems, but also comes with some potential drawbacks that need to be considered. As with any engine technology, it is important to weigh the benefits and drawbacks and choose the right system for your needs.