Direct injection (DI) technology is an advanced fuel delivery system that has become increasingly popular in modern engines due to its efficiency and performance. Unlike traditional fuel injection systems, which inject fuel into the intake manifold before it reaches the engine, direct injection injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber, where it can be precisely controlled and optimized for maximum efficiency.
One of the main advantages of direct injection is its ability to deliver fuel more efficiently than traditional fuel injection systems. Because the fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber, it can be delivered in smaller, more precise amounts, resulting in more complete combustion and improved fuel efficiency. Direct injection also allows for higher fuel pressures, which further improves efficiency and performance.
Direct injection systems typically use a high-pressure fuel pump to deliver fuel to the injectors at pressures of up to 2,000 PSI or more. The injectors themselves are precision-engineered components that use electromagnetic solenoids to open and close the fuel ports with extreme precision, allowing for highly accurate and repeatable fuel delivery.
Another advantage of direct injection is its ability to improve engine performance. By delivering fuel directly into the combustion chamber, direct injection allows for a more complete burn of the fuel-air mixture, resulting in increased power and torque output. This improved combustion also reduces harmful emissions, making direct injection a more environmentally friendly option.
However, direct injection systems also have some drawbacks to consider. For one, they are typically more complex and expensive than traditional fuel injection systems. They also require more frequent maintenance, as the high-pressure fuel system can be more prone to issues like leaks and clogs. Additionally, direct injection engines may require higher-octane fuels to operate properly, which can add to the cost of ownership.
Despite these drawbacks, direct injection remains a popular and effective fuel delivery technology in modern engines. Its efficiency and performance benefits make it a popular choice for many drivers, especially those looking for high-performance vehicles with excellent fuel economy. As technology continues to advance, it’s likely that direct injection will only become more advanced and widely used in the future.
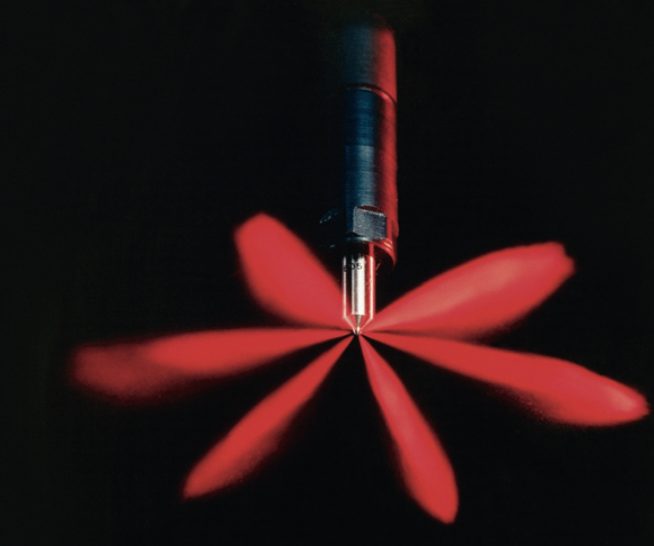
One of the primary advantages of direct injection is its ability to improve fuel efficiency. Direct injection allows for more precise control over the fuel-air mixture, which means that engines can run leaner, using less fuel while still maintaining optimal performance. The precision control of fuel delivery also means that less fuel is wasted during the combustion process, resulting in less emissions and a cleaner burn.
Another advantage of direct injection is that it allows for greater control over the combustion process itself. By injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber, the fuel can be more precisely timed and controlled, leading to more complete combustion and less wasted fuel. This increased control over combustion also allows for improved power output and torque, as the engine can be more finely tuned to optimize performance.
However, there are some drawbacks to direct injection as well. For one, direct injection systems tend to be more complex and expensive than traditional fuel injection systems. This is due in part to the higher fuel pressures required for direct injection, as well as the need for more precise injectors and fuel delivery systems.
Additionally, direct injection systems can be more prone to certain issues like carbon buildup on the intake valves. In traditional fuel injection systems, fuel is sprayed onto the intake valves, which helps to clean them. In direct injection systems, however, the fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber, which means that the intake valves may not be cleaned as thoroughly. Over time, this can lead to carbon buildup on the valves, which can cause engine problems like reduced power and poor fuel economy.
Despite these challenges, direct injection remains a popular and effective fuel delivery technology in modern engines. As engine technology continues to advance, it’s likely that we’ll see even more advanced direct injection systems that offer even greater efficiency, power, and control over the combustion process.
Advantages:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Direct injection allows for more precise control over the fuel-air mixture, resulting in more complete combustion and improved fuel efficiency.
- Increased Power Output: Direct injection engines can be more finely tuned to optimize performance, resulting in increased power and torque output.
- Better Emissions: Direct injection engines tend to produce fewer harmful emissions than traditional fuel injection systems, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
- Higher Fuel Pressure: Direct injection systems can use higher fuel pressures, which allows for more efficient fuel delivery and improved performance.
- Reduced Engine Knock: Direct injection engines tend to experience less engine knock, which is a type of abnormal combustion that can damage the engine.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: Direct injection systems tend to be more complex and expensive than traditional fuel injection systems, which can add to the cost of vehicle ownership.
- Maintenance Requirements: Direct injection engines require more frequent maintenance, as the high-pressure fuel system can be more prone to issues like leaks and clogs.
- Carbon Buildup: Direct injection engines can be more prone to carbon buildup on the intake valves, which can cause engine problems like reduced power and poor fuel economy.
- Higher Octane Fuel Required: Direct injection engines may require higher-octane fuels to operate properly, which can add to the cost of ownership.
- More Complex Repairs: Direct injection systems can be more complex to repair, which can result in higher repair costs and longer repair times.




