Diesel engines are a popular choice for many applications, from heavy-duty trucks to agricultural machinery, due to their high efficiency and durability. One key component that makes diesel engines so efficient is the fuel injection system. In this blog, we will take a closer look at the components of diesel fuel injection systems and how they work together to deliver fuel to the engine.
Fuel injection system overview:
The fuel injection system in a diesel engine is responsible for delivering fuel to the engine at the right time and in the right quantity. It is made up of several components that work together to achieve this. These components include the fuel tank, fuel filter, high-pressure fuel pump, fuel injectors, fuel pressure regulator, and electronic control module (ECM).
Fuel tank:
The fuel tank is the storage unit for diesel fuel. It can be made of various materials such as plastic or metal and is usually located near the rear of the vehicle.
Fuel filter:
The fuel filter is responsible for removing any impurities or contaminants from the diesel fuel before it enters the engine. This helps to protect the fuel injection system and prevent damage to the engine.
High-pressure fuel pump:
The high-pressure fuel pump is responsible for delivering fuel to the fuel injectors at the right pressure. It is driven by a camshaft or the engine’s crankshaft and is typically located in the engine compartment.
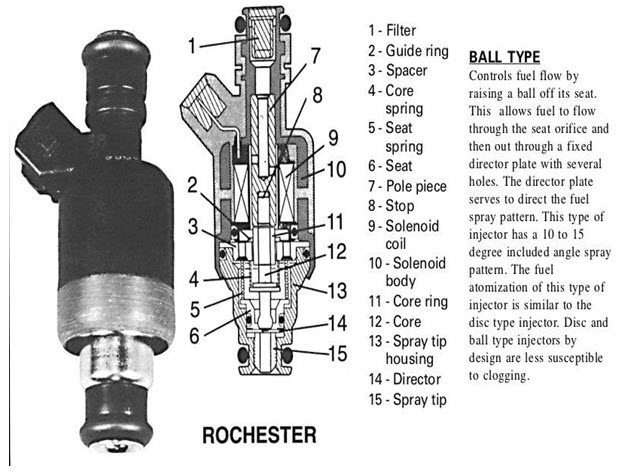
Fuel injectors:
Fuel injectors are responsible for delivering the right amount of fuel to the engine’s combustion chambers. They do this by spraying a fine mist of fuel into the cylinder at the right time. Fuel injectors can be of different types, such as mechanical or electronic injectors, depending on the specific engine’s design.
Fuel pressure regulator:
The fuel pressure regulator helps to regulate the fuel pressure in the fuel injection system. It does this by adjusting the fuel pressure in response to the engine’s needs.
Electronic control module (ECM):
The electronic control module (ECM) is the “brain” of the fuel injection system. It receives input signals from various sensors throughout the engine and adjusts the fuel injection system’s operation accordingly. This helps to ensure that the engine operates efficiently and reliably.
How does the fuel injection system work?
The fuel injection system in a diesel engine works by delivering fuel to the engine’s combustion chambers at the right time and in the right quantity. This is achieved through a process called injection timing and fuel metering.
Injection timing:
Injection timing refers to the precise timing of when the fuel is injected into the engine’s combustion chambers. It is critical to the engine’s performance, as injecting the fuel too early or too late can lead to poor fuel efficiency and increased emissions.
Fuel metering:
Fuel metering refers to the amount of fuel that is injected into the engine’s combustion chambers. It is determined by factors such as the engine’s speed and load, as well as the driver’s input. The fuel pressure regulator and ECM work together to adjust the fuel metering in response to the engine’s needs.
In conclusion, the fuel injection system is a critical component of diesel engines, and its proper functioning is essential for the engine’s performance and reliability. By understanding the different components of the fuel injection system and how they work together, you can better appreciate the complexity and importance of this system in diesel engines.
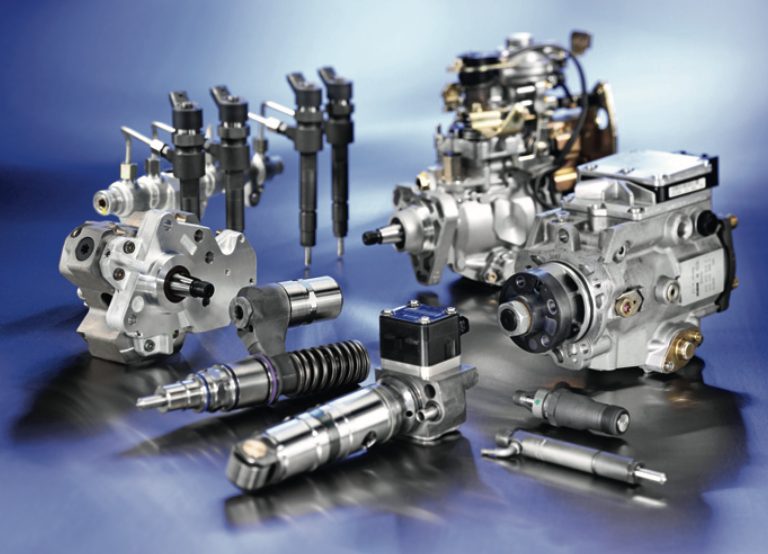

High-pressure fuel pump:
The high-pressure fuel pump is one of the most critical components of the fuel injection system. Its primary function is to generate the high-pressure fuel that is required for injection into the engine’s combustion chamber. The fuel pump typically has a piston that moves back and forth, driven by a camshaft or the engine’s crankshaft. This piston creates a high-pressure fuel flow that is directed to the fuel injectors.
Fuel injectors:
The fuel injectors are responsible for injecting the fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber at the right time and in the right quantity. They are usually located on the cylinder head and have a nozzle that sprays a fine mist of fuel into the cylinder. The fuel injector has a solenoid that is controlled by the ECM, which opens the injector’s valve to allow fuel to flow through it. The nozzle’s size and shape, as well as the fuel pressure, determine the fuel’s injection pattern.
Electronic control module (ECM):
The ECM is the computer that controls the fuel injection system’s operation. It receives input signals from various sensors, such as the engine speed sensor, accelerator pedal position sensor, and air intake temperature sensor, to determine the engine’s operating conditions. Based on these inputs, the ECM adjusts the fuel injection timing and metering to optimize the engine’s performance and efficiency. It also monitors the fuel injection system’s operation and can detect any faults or malfunctions.
Fuel pressure regulator:
The fuel pressure regulator helps to regulate the fuel pressure in the fuel injection system. It is usually located on the fuel rail and has a diaphragm that responds to changes in fuel pressure. If the fuel pressure is too high, the regulator opens to release excess fuel back to the fuel tank. If the fuel pressure is too low, the regulator restricts the fuel flow to maintain the desired pressure.
Fuel filter:
The fuel filter is essential in preventing any contaminants or impurities from entering the fuel injection system. Diesel fuel can contain various impurities, such as dirt, water, and rust particles, that can damage the fuel injectors and other components of the fuel injection system. The fuel filter traps these impurities before they reach the fuel injectors, preventing any potential damage.
Injection timing:
Injection timing is the process of determining when to inject fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber. It is crucial for achieving efficient combustion and minimizing emissions. The injection timing depends on various factors, such as the engine speed, load, and temperature. The ECM calculates the optimal injection timing based on the input signals from the engine sensors.
Fuel metering:
Fuel metering is the process of determining how much fuel to inject into the engine’s combustion chamber. The amount of fuel required depends on various factors, such as the engine’s speed, load, and temperature. The fuel pressure regulator and ECM work together to adjust the fuel metering to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
In conclusion, the fuel injection system is a complex and critical component of diesel engines. Its proper functioning is essential for the engine’s performance, efficiency, and reliability. By understanding the different components of the fuel injection system and how they work together, you can appreciate the importance of proper maintenance and care to ensure the fuel injection system’s longevity and reliability.
Advantages:
- Fuel efficiency: Diesel engines are known for their high fuel efficiency due to the efficient combustion process and the use of diesel fuel injection systems. The fuel injection system meters the fuel precisely, ensuring that the engine receives the exact amount of fuel required for optimal performance.
- Lower emissions: Diesel fuel injection systems are designed to minimize emissions, making diesel engines a more environmentally friendly option than gasoline engines. The precise fuel metering and injection timing help reduce the amount of unburned fuel that escapes through the exhaust.
- Durability: Diesel engines are known for their durability and longevity. The fuel injection system plays a critical role in this as it helps keep the engine running smoothly by providing the precise amount of fuel required for optimal combustion.
- Power output: Diesel engines typically produce more torque and power than gasoline engines, thanks to the efficient combustion process facilitated by the fuel injection system.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Diesel fuel injection systems are typically more expensive than gasoline fuel injection systems due to their complexity and the high pressure required for diesel fuel injection.
- Maintenance: Diesel fuel injection systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This can be more costly and time-consuming than maintaining gasoline fuel injection systems.
- Noise and vibration: Diesel engines are known for their noise and vibration, which can be attributed to the high pressure and combustion process facilitated by the fuel injection system.
- Complexity: Diesel fuel injection systems are more complex than gasoline fuel injection systems, with more components and sensors that can fail or malfunction, requiring diagnosis and repair by a skilled technician.
Overall, while diesel fuel injection systems have some disadvantages, their advantages outweigh them, making them a popular choice for heavy-duty applications such as trucks and industrial equipment, where durability, efficiency, and power output are essential.