A coolant thermistor, also known as a coolant temperature sensor, is a device used to measure the temperature of the engine coolant in a car or other motorized vehicle. This sensor plays an important role in the operation of the engine and can impact its performance if it fails or malfunctions. In this blog, we will discuss the coolant thermistor in more detail, including its function, importance, and potential issues.
Function of Coolant Thermistor:
The primary function of a coolant thermistor is to measure the temperature of the engine coolant and send that information to the engine control module (ECM). The ECM uses this information to adjust the fuel injection and ignition timing, which ultimately affects the engine’s performance and efficiency. If the coolant is too hot or too cold, the ECM will adjust the engine’s operation to compensate for the temperature.
Importance of Coolant Thermistor:
The coolant thermistor is an essential component in modern engine management systems. It provides critical data to the ECM that allows the engine to operate at optimal efficiency and performance. Without accurate temperature data, the ECM may not be able to adjust the engine’s operation correctly, leading to reduced fuel economy, increased emissions, and decreased power output. Furthermore, if the coolant temperature is too high, the engine can overheat, causing significant damage or even complete engine failure.
Issues with Coolant Thermistor:
Like any other component, the coolant thermistor can fail or malfunction over time. A faulty thermistor can cause several problems, such as incorrect temperature readings, engine performance issues, and check engine lights. One common issue is a failed thermistor that reports an incorrect temperature to the ECM, leading to incorrect fuel injection and ignition timing. This can cause reduced fuel economy, increased emissions, and decreased power output. Another common issue is a damaged connector or wiring harness that can cause intermittent connections, leading to incorrect temperature readings or complete sensor failure.
Conclusion:
In summary, the coolant thermistor is a critical component in modern engine management systems that provides the ECM with accurate temperature data. A faulty thermistor can cause several issues, such as reduced fuel economy, increased emissions, and decreased power output. Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent potential issues with the coolant thermistor, ensuring that your engine operates at optimal efficiency and performance. If you notice any symptoms of a failed thermistor, such as a check engine light or engine performance issues, it’s essential to have it diagnosed and repaired promptly to prevent further damage or engine failure.
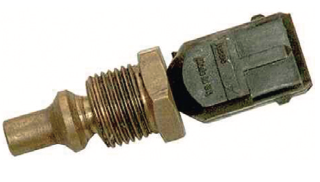
The coolant thermistor is typically located near the engine’s thermostat housing or in the engine block, where it can accurately measure the temperature of the coolant as it circulates through the engine. It works by using a thermistor, which is a type of resistor that changes its resistance in response to changes in temperature. As the temperature of the coolant changes, the resistance of the thermistor changes, which alters the voltage signal that the sensor sends to the ECM.
The ECM uses this information to adjust the fuel injection and ignition timing to ensure that the engine is running efficiently and safely. For example, if the engine is cold, the ECM will enrich the fuel mixture to help it start and warm up faster. As the engine warms up, the ECM will gradually reduce the amount of fuel injected to maintain the correct air/fuel ratio.
One potential issue with the coolant thermistor is that it can become contaminated with debris or rust, which can cause it to read incorrectly or fail altogether. Another issue is that the wiring harness or connector can become damaged, causing an intermittent connection or a complete failure of the sensor.
If you suspect that your coolant thermistor may be failing, there are a few symptoms that you can look for. The most common symptom is a check engine light, which can indicate that there is a problem with the sensor or another component in the engine management system. Other symptoms may include poor fuel economy, decreased power output, rough idling, or difficulty starting the engine when it is cold.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to have your vehicle diagnosed by a qualified mechanic who can determine the cause of the problem and make the necessary repairs. Regular maintenance, such as coolant flushes and inspections, can also help prevent issues with the coolant thermistor by ensuring that the coolant is clean and free of debris.
Advantages:
- Accurate Temperature Measurement: A coolant thermistor provides an accurate measurement of the engine coolant temperature, which allows the engine control module (ECM) to adjust the fuel injection and ignition timing precisely. This can result in improved engine performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions.
- Reliable: The thermistor is a solid-state device with no moving parts, which makes it more reliable than other types of temperature sensors, such as a bi-metallic strip.
- Cost-Effective: Coolant thermistors are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of temperature sensors, which makes them a cost-effective solution for measuring engine coolant temperature.
- Easy to Replace: If a coolant thermistor fails, it is relatively easy to replace, and most mechanics can replace it quickly and without the need for specialized tools.
Disadvantages:
- Vulnerable to Contamination: Coolant thermistors can be vulnerable to contamination from rust, debris, and other contaminants that can cause the sensor to read inaccurately or fail altogether.
- Electrical Issues: Like any electronic component, the coolant thermistor can be susceptible to wiring or connector issues, which can cause intermittent or complete failure of the sensor.
- Limited Functionality: While a coolant thermistor is essential for measuring engine coolant temperature, it has limited functionality beyond that. It cannot measure other engine parameters, such as oil pressure or exhaust gas temperature.
- Can Trigger Check Engine Light: If a coolant thermistor fails or reads incorrectly, it can trigger the check engine light, which can be frustrating for the driver and may require a trip to the mechanic.
In conclusion, the coolant thermistor is an essential component in modern engine management systems, providing accurate temperature data to the ECM, which allows the engine to run efficiently and safely. While it has some disadvantages, such as vulnerability to contamination and electrical issues, it remains a cost-effective and reliable solution for measuring engine coolant temperature.




