A cooling system is an essential component of any machine that generates heat during its operation. Without proper cooling, the excess heat can cause damage to the machine, leading to reduced performance, increased energy consumption, and even total system failure. In this blog post, we will discuss the basic components and functions of a cooling system.
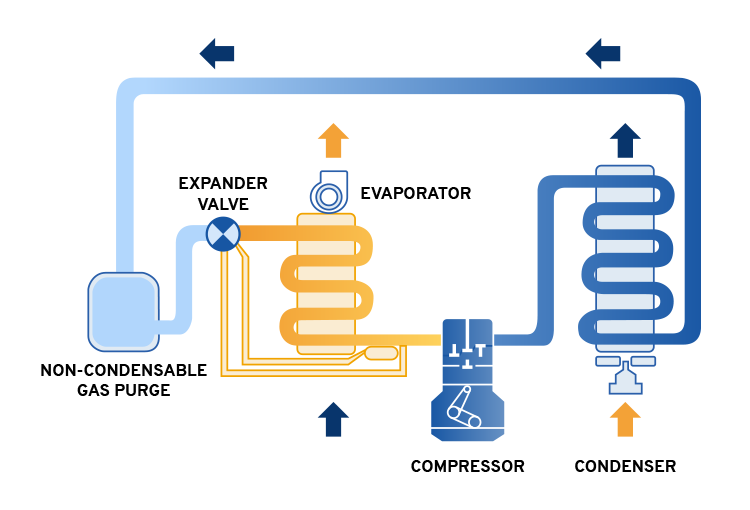
Components of a Basic Cooling System:
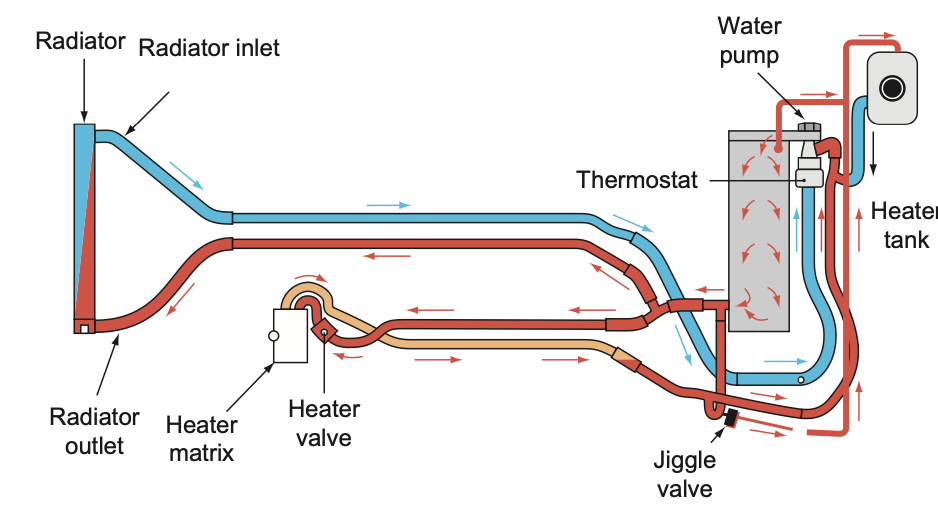
- Radiator: The radiator is the primary component of the cooling system. Its job is to transfer heat from the engine coolant to the air passing through the radiator.
- Water Pump: The water pump is responsible for circulating the coolant through the engine and the radiator.
- Thermostat: The thermostat is a valve that regulates the flow of coolant to the radiator. It opens and closes based on the temperature of the engine, allowing coolant to flow when the engine is hot and restricting the flow when the engine is cold.
- Cooling Fan: The cooling fan is responsible for pulling air through the radiator to dissipate heat from the coolant.
- Hoses: Hoses connect the various components of the cooling system, allowing the coolant to flow from the engine to the radiator and back.
How does a Basic Cooling System Work?
The cooling system works by circulating coolant through the engine and the radiator. As the engine runs, it generates heat, which is absorbed by the coolant. The coolant is then pumped through the radiator, where it is cooled by the air passing through the radiator fins. The cooled coolant is then pumped back to the engine to absorb more heat, and the cycle repeats.
The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant through the engine and the radiator. When the engine is cold, the thermostat is closed, restricting the flow of coolant to the radiator. This allows the engine to warm up quickly. Once the engine reaches the operating temperature, the thermostat opens, allowing coolant to flow through the radiator to be cooled.
The cooling fan is typically activated by a temperature sensor that detects when the coolant temperature is too high. The fan pulls air through the radiator, increasing the rate of heat transfer from the coolant to the air.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a basic cooling system is a critical component of any machine that generates heat during operation. It consists of a radiator, water pump, thermostat, cooling fan, and hoses. The cooling system works by circulating coolant through the engine and the radiator to dissipate heat. The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant, while the cooling fan increases the rate of heat transfer from the coolant to the air passing through the radiator. By understanding the basic components and functions of a cooling system, you can better maintain and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Types of Cooling Systems:
There are two main types of cooling systems: air-cooled and liquid-cooled. In air-cooled systems, the engine is cooled by air passing over fins on the exterior of the engine. This type of system is commonly found in smaller engines, such as those found in lawnmowers and motorcycles. Liquid-cooled systems are more common in larger engines, such as those found in cars and trucks. In liquid-cooled systems, a liquid coolant is circulated through the engine and the radiator to dissipate heat.
Importance of Cooling Systems:
The main purpose of a cooling system is to prevent the engine from overheating. Overheating can cause serious damage to the engine, leading to reduced performance, increased energy consumption, and even total system failure. It is essential to maintain the cooling system to ensure proper operation and prevent costly repairs.
Common Cooling System Issues:
Some common issues that can arise in a cooling system include leaks, clogs, and faulty components. Leaks can occur in the hoses, radiator, or water pump, causing a loss of coolant and decreased performance. Clogs can occur in the radiator or hoses, preventing the coolant from flowing freely and leading to overheating. Faulty components, such as a broken thermostat or malfunctioning cooling fan, can also cause overheating and decreased performance.
Maintaining a Cooling System:
To maintain a cooling system, it is important to regularly check the coolant level and inspect the hoses and radiator for leaks or damage. It is also recommended to flush the system and replace the coolant every 30,000 to 50,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer. Additionally, it is important to have the thermostat, water pump, and cooling fan inspected and replaced as needed.
In conclusion, a cooling system is a critical component of any machine that generates heat during operation. Understanding the basic components and functions of a cooling system can help you better maintain and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. Regular maintenance and inspection can help prevent costly repairs and ensure proper operation.
Advantages of a Cooling System:
- Prevents Overheating: The primary advantage of a cooling system is that it prevents the engine from overheating. Overheating can cause serious damage to the engine, leading to reduced performance, increased energy consumption, and even total system failure.
- Increases Efficiency: A properly functioning cooling system can increase the efficiency of the engine by regulating the temperature and preventing excessive heat buildup.
- Increases Engine Lifespan: By preventing overheating and reducing wear and tear on engine components, a cooling system can increase the lifespan of the engine and reduce the need for costly repairs.
Disadvantages of a Cooling System:
- Complexity: Cooling systems can be complex and require regular maintenance and inspection to ensure proper operation. Faulty components or leaks can cause decreased performance or even total system failure.
- Increased Weight and Complexity: Liquid-cooled systems, in particular, can add weight and complexity to the engine and may require additional components such as a radiator, water pump, and hoses.
- Increased Energy Consumption: Cooling systems can increase energy consumption, as the fan and water pump require energy to operate. This can lead to decreased fuel efficiency in some cases.
In conclusion, while cooling systems offer many advantages such as preventing engine overheating, increasing efficiency, and increasing the lifespan of the engine, they can also have disadvantages such as complexity, increased weight and complexity, and increased energy consumption. It is important to maintain and inspect the cooling system regularly to ensure proper operation and prevent costly repairs.