A boost control system is an important component of a turbocharged engine, which helps regulate and control the amount of boost pressure produced by the turbocharger. The boost pressure refers to the amount of compressed air that is forced into the engine’s cylinders, which ultimately results in increased engine performance and power.
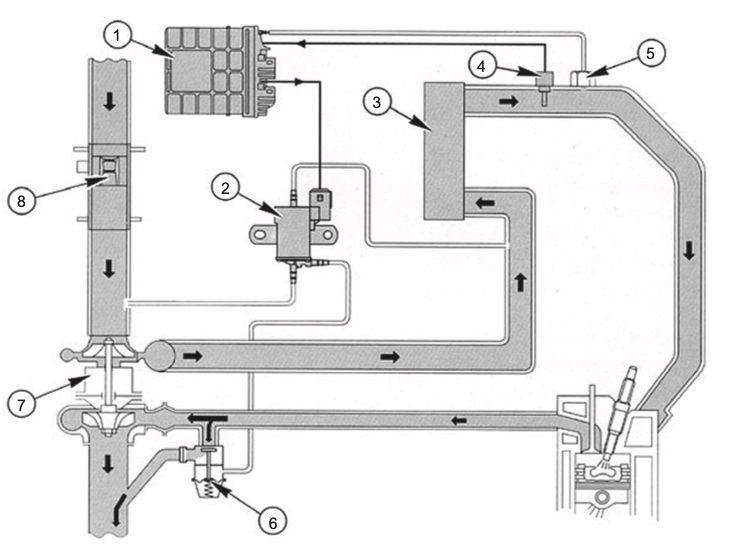
A boost control system works by using a combination of mechanical and electronic components to regulate the amount of boost pressure produced by the turbocharger. The main components of a boost control system include a wastegate, boost controller, and solenoid valve.
The wastegate is a valve that is connected to the exhaust system and the turbocharger. It is designed to open and release exhaust gases when the pressure inside the turbocharger reaches a certain level. This prevents the turbocharger from producing too much boost pressure, which can cause engine damage.
The boost controller is the device that regulates the amount of boost pressure produced by the turbocharger. It can be either manual or electronic and works by adjusting the amount of pressure that is sent to the wastegate. When the boost controller senses that the desired boost pressure has been reached, it signals the wastegate to open and release exhaust gases.
The solenoid valve is an electronic valve that controls the amount of pressure that is sent to the wastegate. It receives signals from the boost controller and adjusts the pressure accordingly. It is an essential component of an electronic boost control system and allows for more precise control over the boost pressure produced by the turbocharger.
There are two main types of boost control systems: manual and electronic. Manual boost control systems use a mechanical device to adjust the amount of boost pressure produced by the turbocharger. They are typically less expensive than electronic boost control systems but can be less precise and more difficult to adjust.
Electronic boost control systems, on the other hand, use electronic components to adjust the boost pressure. They are more precise and easier to adjust than manual systems, but they are also more expensive.
Overall, a boost control system is an essential component of a turbocharged engine. It allows for precise control over the amount of boost pressure produced by the turbocharger, which can result in increased engine performance and power. Whether you choose a manual or electronic system, it is important to ensure that your boost control system is properly installed and adjusted to avoid engine damage and to optimize your engine’s performance.
As mentioned earlier, the boost pressure refers to the amount of compressed air that is forced into the engine’s cylinders. The amount of boost pressure that a turbocharger produces is directly proportional to the speed of the turbine, which is driven by the exhaust gases from the engine.
When the throttle is opened, the engine demands more air to produce more power. As a result, the turbocharger spins faster and produces more boost pressure. However, if the boost pressure gets too high, it can cause engine damage. This is where the boost control system comes in.
The wastegate is a valve that is designed to open and release exhaust gases when the pressure inside the turbocharger reaches a certain level. The wastegate can be either internal or external. Internal wastegates are built into the turbocharger housing, while external wastegates are mounted separately and connected to the turbocharger by a pipe.
The wastegate is connected to a boost controller, which regulates the amount of boost pressure produced by the turbocharger. The boost controller can be either manual or electronic.
A manual boost controller is a mechanical device that is typically installed between the turbocharger and the wastegate. It uses a spring-loaded valve to regulate the amount of pressure that is sent to the wastegate. The user can adjust the boost pressure by turning a knob on the controller.
An electronic boost controller, on the other hand, uses electronic components to regulate the boost pressure. It typically consists of a solenoid valve, a pressure sensor, and a control unit. The solenoid valve controls the amount of pressure that is sent to the wastegate, while the pressure sensor measures the boost pressure. The control unit receives signals from the pressure sensor and adjusts the solenoid valve accordingly to maintain the desired boost pressure.
Electronic boost controllers offer more precise control over the boost pressure, which can result in better performance and increased efficiency. However, they are more expensive than manual controllers.
In addition to the wastegate and boost controller, some turbocharged engines may also use a blow-off valve (BOV) or a bypass valve (BPV). These valves are designed to release the excess pressure that builds up in the intake system when the throttle is closed, such as during gear changes or when coasting. Without a BOV or BPV, the excess pressure can cause the turbocharger to stall or even reverse its direction of rotation, which can cause damage.
Overall, a boost control system is an essential component of a turbocharged engine. It allows for precise control over the amount of boost pressure produced by the turbocharger, which can result in increased engine performance and power. It is important to ensure that your boost control system is properly installed and adjusted to avoid engine damage and to optimize your engine’s performance.
Advantages:
- Increased engine performance and power: A boost control system allows for precise control over the amount of boost pressure produced by the turbocharger. By optimizing the boost pressure, the engine can produce more power and better performance.
- Improved fuel efficiency: By optimizing the boost pressure, the engine can operate more efficiently, resulting in improved fuel efficiency.
- Customizable: Boost control systems can be customized to meet the specific needs of a particular engine. For example, different boost levels can be set for different driving conditions, such as highway driving or racing.
- Better control over engine behavior: A boost control system can be used to control the behavior of the engine under various conditions, such as load, temperature, and altitude.
- Easy to install: Boost control systems are generally easy to install and can be done by a skilled mechanic.
Disadvantages:
- Increased complexity: A boost control system adds complexity to the engine, which can increase the chances of component failure and maintenance requirements.
- Cost: Boost control systems can be expensive, especially if an electronic boost control system is used.
- Requires tuning: A boost control system requires tuning to ensure that the engine operates optimally. This can be time-consuming and may require specialized knowledge and equipment.
- Can cause engine damage: If a boost control system is not properly installed or tuned, it can cause engine damage, including blown head gaskets, damaged pistons, and bent connecting rods.
- May affect emissions: If the boost pressure is increased beyond the manufacturer’s specifications, it may cause the engine to produce more emissions than allowed by law.
Overall, a boost control system can provide significant benefits to a turbocharged engine. However, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks and ensure that the system is properly installed, maintained, and tuned to avoid engine damage and ensure optimal performance.




