Roller cell pumps, also known as rotary lobe pumps, are positive displacement pumps that are widely used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications. They are particularly useful for pumping high viscosity fluids, slurries, and liquids containing solids or abrasive materials. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at how roller cell pumps work and what makes them so effective.
How Roller Cell Pumps Work:
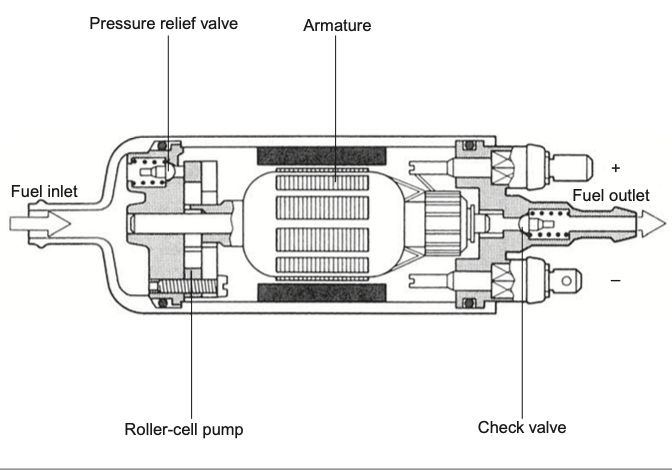
Roller cell pumps consist of two rotors with lobes that rotate inside a specially designed casing. The rotors are mounted on separate shafts that are synchronized by gears or timing belts. As the rotors turn, the lobes trap fluid between them and the casing, creating a series of pockets that move the fluid from the inlet to the outlet of the pump.
One of the unique features of roller cell pumps is the use of rollers that ride on the rotor lobes. These rollers maintain a tight seal between the rotors and the casing, preventing fluid from leaking back into the inlet or outlet. The rollers also reduce friction and wear between the lobes and casing, making roller cell pumps more durable than other types of positive displacement pumps.
Advantages of Roller Cell Pumps:
- High Efficiency – Roller cell pumps are highly efficient and can deliver consistent flow rates and pressures over a wide range of operating conditions.
- Gentle Handling – Roller cell pumps are gentle on delicate or shear-sensitive fluids, making them ideal for handling high-value or sensitive products.
- Versatility – Roller cell pumps can handle a wide range of fluids, including high viscosity fluids, slurries, and liquids containing solids or abrasive materials.
- Low Maintenance – Roller cell pumps have a simple design with few moving parts, which means they require minimal maintenance and can operate for long periods without the need for repairs.
Applications of Roller Cell Pumps:
Roller cell pumps are used in a wide variety of industries, including food and beverage, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, mining, and wastewater treatment. Some common applications of roller cell pumps include:
- Food and Beverage Processing – Roller cell pumps are used to transfer high viscosity fluids, such as syrups, sauces, and pastes, in food and beverage processing plants.
- Chemical Processing – Roller cell pumps are used to handle corrosive and abrasive fluids, such as acids, alkalis, and solvents, in chemical processing plants.
- Pharmaceuticals – Roller cell pumps are used to transfer highly viscous and shear-sensitive fluids, such as ointments, creams, and gels, in pharmaceutical production.
- Mining – Roller cell pumps are used to transfer slurry and tailings in mining operations.
Conclusion:
Roller cell pumps are highly efficient and versatile positive displacement pumps that are widely used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications. Their unique design, which includes rollers that ride on the rotor lobes, makes them highly reliable and durable. Roller cell pumps are ideal for pumping high viscosity fluids, slurries, and liquids containing solids or abrasive materials, and are gentle on delicate or shear-sensitive fluids.
One of the reasons why roller cell pumps are so efficient is because they are positive displacement pumps. Positive displacement pumps move a fixed volume of fluid per rotation or cycle, regardless of changes in pressure or viscosity. This makes them ideal for applications where precise flow rates and pressures are required. Roller cell pumps are particularly useful for handling high viscosity fluids because they can generate high levels of shear, which helps to break down the fluid and reduce its viscosity.
In addition to their high efficiency, roller cell pumps are also known for their gentle handling of fluids. Unlike some other types of pumps, roller cell pumps do not rely on impellers or vanes that can cause shear and turbulence in the fluid. Instead, the lobes on the rotors of the roller cell pump create a smooth, steady flow that minimizes shear and turbulence. This makes roller cell pumps ideal for handling delicate or shear-sensitive fluids, such as emulsions, suspensions, and biological fluids.
Roller cell pumps can be made from a variety of materials, including stainless steel, cast iron, and plastic. The choice of material depends on the specific application and the type of fluid being pumped. For example, stainless steel is often used in food and beverage processing because it is easy to clean and does not corrode. Plastic is often used in chemical processing because it is resistant to corrosive chemicals.
Overall, roller cell pumps are versatile and reliable pumps that can handle a wide range of fluids and operating conditions. They are ideal for applications where precise flow rates and pressures are required, and where gentle handling of fluids is important. Roller cell pumps are used in a variety of industries, including food and beverage processing, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, mining, and wastewater treatment.
Advantages:
- High Efficiency: Roller cell pumps are highly efficient and can deliver consistent flow rates and pressures over a wide range of operating conditions.
- Gentle Handling: Roller cell pumps are gentle on delicate or shear-sensitive fluids, making them ideal for handling high-value or sensitive products.
- Versatility: Roller cell pumps can handle a wide range of fluids, including high viscosity fluids, slurries, and liquids containing solids or abrasive materials.
- Low Maintenance: Roller cell pumps have a simple design with few moving parts, which means they require minimal maintenance and can operate for long periods without the need for repairs.
- Self-Priming: Roller cell pumps are self-priming, which means they can create suction and lift fluid from below the pump inlet without the need for a separate priming system.
- Reversible Flow: Roller cell pumps can operate in both directions, allowing for reversible flow and easy cleaning.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Pressure: Roller cell pumps have a limited maximum pressure, typically up to 20 bar, which may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Limited Flow Range: Roller cell pumps have a limited flow range, typically up to 200 m3/h, which may not be suitable for high-volume applications.
- Limited Solids Handling: While roller cell pumps can handle liquids containing solids or abrasive materials, they are not designed for heavy-duty solids handling applications.
- High Cost: Roller cell pumps can be more expensive than other types of pumps due to their unique design and construction.
- Noise and Vibration: Roller cell pumps can produce noise and vibration during operation, which may require additional noise reduction measures.
- Temperature Limits: Roller cell pumps may have temperature limits depending on the materials used in their construction, which may restrict their use in certain applications.
Overall, roller cell pumps offer many advantages for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. However, like any pump, they also have some limitations that should be considered when selecting the right pump for a particular application.




