Rectifiers are electronic devices used to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). They are widely used in various electronic applications, including power supplies, audio amplifiers, and electronic instrumentation. In this blog, we will explore the different types of rectifiers, their applications, and the advantages and disadvantages of each type.
Types of Rectifiers: There are two types of rectifiers: half-wave and full-wave.
- Half-wave Rectifiers: As the name suggests, a half-wave rectifier is a circuit that rectifies only half of the AC waveform. The half-wave rectifier circuit consists of a single diode, which allows current to flow only during the positive half-cycle of the AC waveform. During the negative half-cycle, the diode blocks the flow of current. This results in a DC output voltage that is half the peak voltage of the input AC waveform. The half-wave rectifier circuit is simple, inexpensive, and widely used in low-power applications.
- Full-wave Rectifiers: Unlike half-wave rectifiers, full-wave rectifiers rectify both the positive and negative half-cycles of the AC waveform. This results in a higher output voltage and smoother DC waveform. There are two types of full-wave rectifiers: center-tapped and bridge rectifiers.
- Center-tapped Full-wave Rectifiers: Center-tapped full-wave rectifiers use a center-tapped transformer and two diodes to rectify both the positive and negative half-cycles of the AC waveform. The center-tap is connected to the ground, and the two diodes are connected to the ends of the secondary winding. During the positive half-cycle, one diode conducts and charges the capacitor, while the other diode blocks the flow of current. During the negative half-cycle, the roles of the diodes are reversed, resulting in a DC output voltage that is equal to the peak voltage of the AC waveform.
- Bridge Rectifiers: Bridge rectifiers use four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration to rectify both the positive and negative half-cycles of the AC waveform. Unlike center-tapped full-wave rectifiers, bridge rectifiers do not require a center-tapped transformer, making them more efficient and less expensive. During the positive half-cycle, two diodes conduct and charge the capacitor, while the other two diodes block the flow of current. During the negative half-cycle, the roles of the diodes are reversed, resulting in a DC output voltage that is equal to the peak voltage of the AC waveform.
Applications: Rectifiers are used in various electronic applications, including:
- Power Supplies: Rectifiers are used in power supplies to convert AC voltage to DC voltage. DC voltage is used to power electronic devices, including computers, televisions, and mobile phones.
- Audio Amplifiers: Rectifiers are used in audio amplifiers to convert the AC signal from the audio source to a DC signal. This DC signal is then amplified and used to drive the speakers.
- Electronic Instrumentation: Rectifiers are used in electronic instrumentation to convert AC signals from sensors to DC signals. This DC signal is then processed and used to display or record data.

Advantages and Disadvantages:
The advantages of rectifiers include:
- Efficient conversion of AC voltage to DC voltage
- Simple circuit design and low cost
- Wide range of applications
The disadvantages of rectifiers include:
- Ripple in the DC output voltage due to the pulsating nature of the rectified waveform
- Inaccurate DC output voltage due to variations in the input AC voltage and load resistance
- Heat dissipation due to the high current flowing through the diodes during rectification.
Conclusion: Rectifiers are essential electronic devices used to convert AC voltage to DC voltage. There are two types of rect
Rectifiers are electronic devices that convert AC voltage to DC voltage. AC voltage is the voltage that oscillates between positive and negative values, while DC voltage has a constant value. The conversion of AC to DC voltage is important in electronic devices because many of them require a constant voltage to function correctly. For example, computer power supplies convert AC voltage from a wall outlet to DC voltage to power the components of the computer.
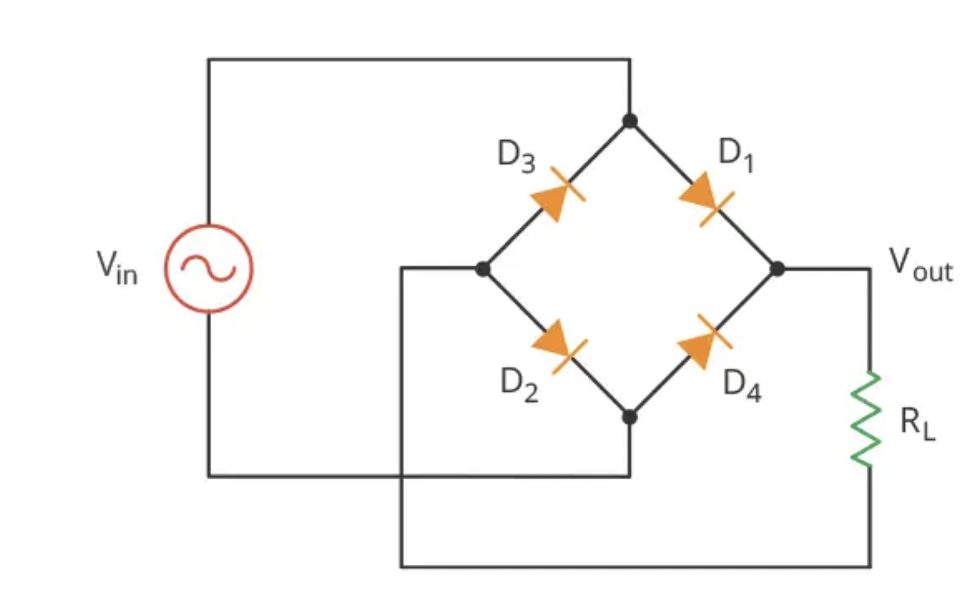
The most common types of rectifiers are the half-wave and full-wave rectifiers. The half-wave rectifier circuit is simple and inexpensive but has some limitations. It only allows the positive half-cycle of the AC voltage to pass, which results in a DC voltage that is half the peak voltage of the AC voltage. The full-wave rectifier overcomes this limitation by using both the positive and negative half-cycles of the AC voltage to produce a smoother and more consistent DC voltage output.
The center-tapped full-wave rectifier uses a center-tapped transformer and two diodes to produce the DC voltage output. The transformer steps down the high-voltage AC signal to a lower voltage that can be used by the diodes. The center-tap of the transformer is grounded, and the two diodes are connected to the ends of the secondary winding. The two diodes conduct in alternation, resulting in a DC voltage output that is equal to the peak voltage of the AC signal.
The bridge rectifier, on the other hand, uses four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration to produce the DC voltage output. The bridge rectifier does not require a center-tapped transformer and is therefore more efficient and less expensive than the center-tapped full-wave rectifier. During the positive half-cycle of the AC voltage, two diodes conduct, and the other two diodes block the flow of current. During the negative half-cycle of the AC voltage, the roles of the diodes are reversed, resulting in a DC voltage output that is equal to the peak voltage of the AC voltage.

One of the limitations of rectifiers is the presence of ripple in the DC voltage output. Ripple is caused by the pulsating nature of the rectified waveform and can be reduced by using capacitors in the circuit. Another limitation is the variation in the DC voltage output due to changes in the input AC voltage and load resistance. Voltage regulators can be used to overcome this limitation and provide a constant voltage output.
In conclusion, rectifiers are essential components in electronic devices that require a constant DC voltage output. They come in different types, each with its advantages and limitations. Understanding the different types of rectifiers and their applications can help you choose the right one for your electronic device.




