An air-cored gauge, also known as an air-core coil or a capacitive displacement sensor, is an instrument used to measure the distance or displacement between two objects. It is a non-contact method of measuring distance that relies on the principle of capacitance.
In an air-cored gauge, two parallel plates are separated by a small air gap. One plate is stationary, while the other is attached to the moving object whose displacement is to be measured. When an AC voltage is applied to the stationary plate, an electric field is generated between the two plates. As the distance between the plates changes due to the movement of the object, the capacitance of the sensor changes, and this change is detected and converted into an electrical signal that can be measured.
Air-cored gauges are commonly used in applications where the accuracy and resolution of the measurement are critical. They can measure distances with high precision, typically on the order of a few nanometers. Air-cored gauges are also highly sensitive and can detect very small changes in displacement. They are often used in scientific research, industrial manufacturing, and engineering applications.
One of the advantages of air-cored gauges is their non-contact nature, which means that they do not need to physically touch the object being measured. This can be useful in situations where contact with the object could cause damage or alter its behavior. Another advantage is that air-cored gauges are highly reliable and require very little maintenance.
However, air-cored gauges also have some limitations. They are sensitive to environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, which can affect the accuracy of the measurements. In addition, the range of the gauge is limited by the distance between the two plates. If the distance exceeds this range, the measurement will no longer be accurate.
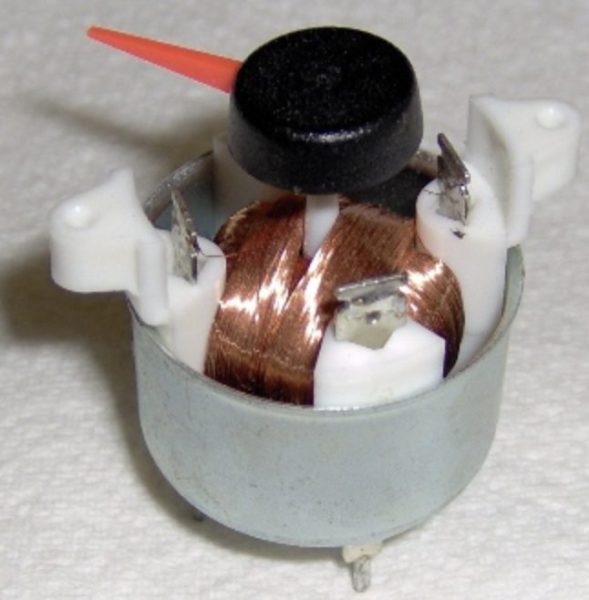

In summary, air-cored gauges are a highly accurate and sensitive method of measuring distance or displacement. They are non-contact and reliable, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. However, they do have some limitations, such as sensitivity to environmental factors and limited range. Overall, air-cored gauges are a valuable tool in many fields, including scientific research, manufacturing, and engineering.
Air-cored gauges operate on the principle of capacitance, which is the ability of a system of conductors to store electrical energy in an electric field. In an air-cored gauge, the two parallel plates act as the conductors, and the air gap between them acts as the dielectric medium.
When an AC voltage is applied to the stationary plate of the gauge, an electric field is generated between the two plates. The electric field stores electrical energy in the form of an electric charge on each plate, which is proportional to the capacitance of the gauge. The capacitance, in turn, depends on the distance between the plates.
As the distance between the plates changes due to the movement of the object being measured, the capacitance of the gauge changes as well. This change in capacitance results in a change in the electrical charge on the plates, which can be detected and converted into an electrical signal that can be measured.
There are several different types of air-cored gauges, including linear variable differential transformers (LVDTs), variable capacitance gauges, and eddy current gauges. Each type has its own unique design and method of operation, but all rely on the principle of capacitance to measure distance or displacement.
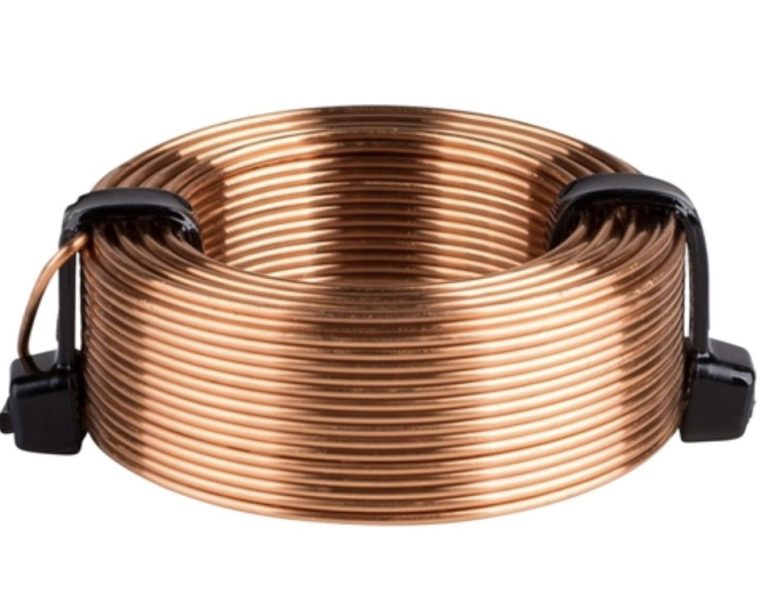

Air-cored gauges have a number of advantages over other types of distance measurement instruments. They are non-contact, which means that they do not require physical contact with the object being measured, reducing the risk of damage or alteration of the object’s behavior. They are also highly accurate and can measure distances with high precision.
However, air-cored gauges do have some limitations. They are sensitive to environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, which can affect the accuracy of the measurements. They also have a limited range, which means that they may not be suitable for measuring large distances.
In conclusion, air-cored gauges are a valuable tool for measuring distance or displacement in a wide range of applications. They rely on the principle of capacitance and are highly accurate and sensitive. While they do have some limitations, their non-contact nature and high precision make them an ideal choice for many scientific, industrial, and engineering applications.
Advantages:
- Non-contact measurement: Air-cored gauges do not require physical contact with the object being measured, which reduces the risk of damage or alteration of the object’s behavior.
- High accuracy: Air-cored gauges can measure distances with high precision, typically on the order of a few nanometers.
- High sensitivity: Air-cored gauges are highly sensitive and can detect very small changes in displacement.
- Reliable: Air-cored gauges are highly reliable and require very little maintenance.
- Wide range of applications: Air-cored gauges can be used in scientific research, industrial manufacturing, and engineering applications.
Disadvantages:
- Sensitivity to environmental factors: Air-cored gauges are sensitive to environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, which can affect the accuracy of the measurements.
- Limited range: The range of the gauge is limited by the distance between the two plates. If the distance exceeds this range, the measurement will no longer be accurate.
- Expensive: Air-cored gauges can be more expensive than other types of distance measurement instruments.
- Complex setup: Air-cored gauges require a complex setup and calibration process, which can make them more difficult to use than other types of instruments.
- Susceptible to interference: Air-cored gauges can be susceptible to interference from other electrical or magnetic sources, which can affect the accuracy of the measurements.
In summary, while air-cored gauges have some limitations, their high accuracy, sensitivity, and reliability make them a valuable tool in many fields.




