Modern cars are equipped with a variety of electronic control units (ECUs) that are responsible for managing various systems such as the engine, transmission, and fuel control. The fuel control ECU, also known as the fuel injection ECU, plays a critical role in managing the fuel delivery system of the vehicle. In this blog, we will discuss the fuel control ECU and its typical inputs and outputs.
What is a Fuel Control ECU?
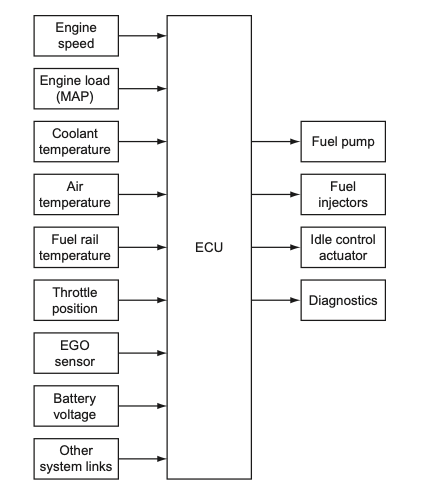
A fuel control ECU is an electronic control unit that manages the fuel delivery system of a vehicle. It uses various inputs from sensors to determine the optimal amount of fuel to be delivered to the engine, and then sends signals to the fuel injectors to open and close at the correct times. This ensures that the engine receives the correct amount of fuel, and runs efficiently and smoothly.
Typical Inputs of a Fuel Control ECU
- Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF)
The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine, which is critical information for determining the correct amount of fuel to be injected. The fuel control ECU receives signals from the MAF sensor and adjusts the fuel injection accordingly.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
The TPS sensor measures the position of the throttle, which is a critical input for determining the engine load. The fuel control ECU uses this information to adjust the fuel injection to match the engine load.
- Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECT)
The ECT sensor measures the temperature of the engine coolant. This information is used by the fuel control ECU to adjust the fuel injection based on the engine’s operating temperature.
- Oxygen Sensor (O2)
The O2 sensor measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas, which is an indicator of the combustion efficiency. The fuel control ECU uses this information to adjust the fuel injection to maintain the optimal air-fuel ratio.
Typical Outputs of a Fuel Control ECU
- Fuel Injectors
The fuel control ECU sends signals to the fuel injectors to open and close at the correct times. This controls the amount of fuel that is injected into the engine.
- Fuel Pump
The fuel control ECU controls the fuel pump to ensure that the correct amount of fuel is delivered to the engine. This is important for maintaining the correct fuel pressure and flow rate.
- Idle Air Control Valve (IACV)
The IACV controls the amount of air that enters the engine when the throttle is closed, such as when the vehicle is idling. The fuel control ECU sends signals to the IACV to maintain the correct idle speed.
Conclusion
The fuel control ECU is a critical component of the vehicle’s fuel delivery system. It receives inputs from various sensors and uses this information to control the fuel injection system. The fuel control ECU also controls other components such as the fuel pump and idle air control valve. By ensuring that the engine receives the correct amount of fuel, the fuel control ECU helps to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
How does a fuel control ECU work?
The fuel control ECU is essentially a small computer that receives input signals from various sensors throughout the vehicle. It uses these signals to calculate the optimal amount of fuel to inject into the engine, based on factors such as the engine load, operating temperature, and air-fuel ratio.
Once the fuel control ECU has determined the correct amount of fuel to inject, it sends signals to the fuel injectors to open and close at the appropriate times. This ensures that the correct amount of fuel is delivered to the engine, based on its current operating conditions.
The fuel control ECU is able to make these calculations in real-time, constantly adjusting the fuel injection to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
What are some common issues with fuel control ECUs?
Like any electronic component, fuel control ECUs can sometimes fail or malfunction. Some common issues that can occur with fuel control ECUs include:
- Faulty sensors – If one of the sensors that provides input to the fuel control ECU is faulty, it can cause incorrect calculations and result in poor engine performance or fuel economy.
- Wiring issues – Problems with the wiring between the sensors and the fuel control ECU can also cause issues with fuel delivery and engine performance.
- Failed fuel injectors – If one or more of the fuel injectors fail, it can cause the engine to run poorly or not start at all.
- Software issues – In some cases, software issues or programming errors can cause the fuel control ECU to malfunction or deliver incorrect fuel injection signals.
- Physical damage – Damage to the fuel control ECU itself, such as from water or heat exposure, can also cause it to malfunction or fail.
Overall, while fuel control ECUs are generally reliable components, it’s important to keep an eye out for any signs of issues and have them addressed promptly by a qualified mechanic.
In conclusion, fuel control ECUs are critical components of modern vehicles that help to ensure optimal fuel delivery and engine performance. By receiving input signals from various sensors and sending signals to the fuel injectors, fuel control ECUs are able to make real-time adjustments to optimize fuel delivery and engine performance. However, like any electronic component, they can sometimes fail or malfunction, so it’s important to be aware of the common issues and have them addressed promptly.
Advantages of Fuel Control ECUs:
- Improved Engine Performance: One of the primary advantages of fuel control ECUs is improved engine performance. By constantly adjusting the fuel injection to optimize engine operation, fuel control ECUs can help to improve power output, acceleration, and overall drivability.
- Better Fuel Economy: Fuel control ECUs are also designed to optimize fuel delivery, which can help to improve fuel economy. By ensuring that the engine is running as efficiently as possible, fuel control ECUs can help to reduce fuel consumption and save money on gas.
- Reduced Emissions: Another benefit of fuel control ECUs is that they can help to reduce emissions. By maintaining the correct air-fuel ratio and optimizing engine performance, fuel control ECUs can help to minimize harmful exhaust emissions.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Fuel control ECUs are able to make real-time adjustments to the fuel injection system, constantly optimizing engine performance based on changing conditions such as engine load and operating temperature.
Disadvantages of Fuel Control ECUs:
- Complexity: Fuel control ECUs are complex electronic components that require specialized knowledge and tools to diagnose and repair. This can make them more difficult and expensive to service than traditional mechanical components.
- Reliability: While fuel control ECUs are generally reliable, they can sometimes fail or malfunction. When this happens, it can cause issues with engine performance and drivability, which can be difficult and expensive to diagnose and repair.
- Compatibility: In some cases, fuel control ECUs may not be compatible with aftermarket performance upgrades or modifications. This can limit the ability of vehicle owners to customize and modify their vehicles.
- Cost: Fuel control ECUs can be expensive to replace, which can be a concern for vehicle owners who need to replace a faulty unit.
Overall, while fuel control ECUs offer a range of benefits in terms of engine performance, fuel economy, and emissions reduction, they can also be complex, expensive, and difficult to service. It’s important for vehicle owners to weigh the pros and cons of fuel control ECUs before deciding whether or not to invest in them.

Comments are closed.