Diesel engines have long been popular for their fuel efficiency and durability, but they have also been criticized for their emissions of harmful pollutants. In response, automotive manufacturers have developed various technologies to reduce diesel emissions, including the use of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems.
What is Diesel Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)?
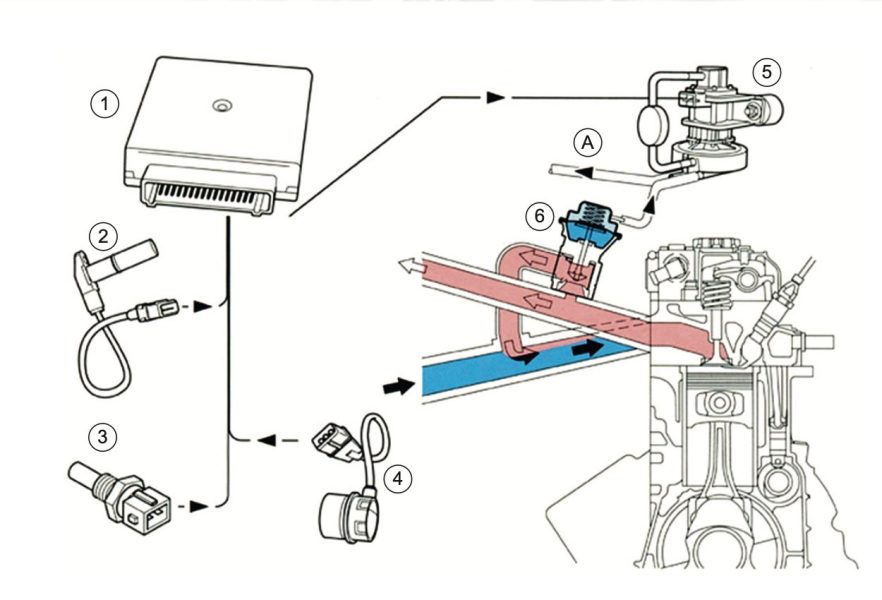
Diesel EGR is a system that recirculates a portion of the engine’s exhaust gases back into the engine’s combustion chamber. The recirculated exhaust gas contains less oxygen than fresh air, which reduces the combustion temperature and lowers the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx), a group of pollutants that contribute to smog and air pollution.
How does Diesel EGR work?
Diesel EGR systems typically use a combination of valves, sensors, and a control unit to regulate the recirculation of exhaust gas. The system works by diverting a portion of the exhaust gases from the exhaust manifold into a cooler or heat exchanger, where it is cooled and filtered to remove soot and other particulate matter.
The cooled exhaust gas is then recirculated back into the engine through the intake manifold, where it mixes with fresh air and fuel before entering the combustion chamber. The proportion of exhaust gas recirculated varies depending on engine operating conditions, with higher recirculation rates used at low engine loads and lower rates at high loads.
What are the benefits of Diesel EGR?
The use of EGR systems in diesel engines can bring significant benefits, including:
- Reduced emissions of NOx: The recirculation of exhaust gas reduces the combustion temperature, which lowers the formation of nitrogen oxides, the primary pollutant emitted by diesel engines.
- Improved fuel efficiency: The recirculation of exhaust gas can improve fuel efficiency by reducing the amount of fuel needed for combustion.
- Enhanced engine performance: By reducing the combustion temperature, EGR systems can reduce the formation of hot spots in the engine, which can damage engine components and reduce overall performance.
- Lowered combustion noise: By reducing the peak combustion temperature and pressure, EGR systems can lower combustion noise, making the engine quieter.
Are there any drawbacks to Diesel EGR?
While EGR systems can bring significant benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks:
- Increased particulate matter emissions: EGR systems can increase the formation of particulate matter, which can be harmful to human health and the environment.
- Increased engine complexity: The addition of an EGR system can increase the complexity of the engine, requiring additional components and maintenance.
- Reduced engine power output: The recirculation of exhaust gas reduces the amount of oxygen available for combustion, which can reduce engine power output.
Conclusion
Diesel EGR is an effective technology for reducing diesel engine emissions of nitrogen oxides, improving fuel efficiency, and enhancing engine performance. However, the use of EGR systems can also have some potential drawbacks, including increased particulate matter emissions, increased engine complexity, and reduced engine power output. Overall, the use of EGR systems in diesel engines is an important step towards reducing the environmental impact of diesel engines while still maintaining their efficiency and durability.
- Types of EGR systems: There are two types of EGR systems used in diesel engines: high-pressure EGR and low-pressure EGR. High-pressure EGR systems recirculate exhaust gas directly from the exhaust manifold, while low-pressure EGR systems recirculate exhaust gas after it has been cooled and filtered through a heat exchanger.
- EGR valves: EGR valves control the flow of exhaust gas into the engine’s intake manifold. There are two types of EGR valves: pneumatic and electric. Pneumatic EGR valves are controlled by engine vacuum, while electric EGR valves are controlled by the engine control module (ECM).
- EGR coolers: EGR coolers are used in low-pressure EGR systems to cool and filter the recirculated exhaust gas. They are typically made of aluminum or stainless steel and use a heat exchanger to transfer heat from the exhaust gas to the engine coolant.
- EGR failure: EGR systems can fail due to a variety of reasons, including clogging of the EGR valve or cooler, damage to the EGR valve or cooler, or malfunction of the EGR control system. EGR failure can result in increased emissions, reduced fuel efficiency, and engine performance issues.
- EGR delete: Some diesel engine owners choose to delete or remove their EGR systems in order to increase engine power output and performance. However, EGR deletion is illegal in many jurisdictions and can result in fines or penalties for violating emissions regulations.
In summary, diesel exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is a technology that reduces diesel engine emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by recirculating a portion of exhaust gas back into the engine’s combustion chamber. EGR systems can improve fuel efficiency, enhance engine performance, and reduce combustion noise, but they can also increase particulate matter emissions and engine complexity, and reduce engine power output. It’s important to maintain and repair EGR systems properly to ensure they function correctly and meet emissions regulations.
Advantages of Diesel Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR):
- Reduces NOx emissions: EGR systems reduce the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx), a group of pollutants that contribute to smog and air pollution. This helps diesel engines meet emissions regulations and reduce their environmental impact.
- Improves fuel efficiency: EGR systems can improve fuel efficiency by reducing the amount of fuel needed for combustion. This leads to lower fuel costs and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Enhances engine performance: By reducing the formation of hot spots in the engine, EGR systems can enhance engine performance and improve engine durability.
- Lowers combustion noise: EGR systems can lower combustion noise by reducing the peak combustion temperature and pressure.
Disadvantages of Diesel Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR):
- Increases particulate matter emissions: EGR systems can increase the formation of particulate matter, which can be harmful to human health and the environment.
- Increases engine complexity: The addition of an EGR system can increase the complexity of the engine, requiring additional components and maintenance.
- Reduces engine power output: The recirculation of exhaust gas reduces the amount of oxygen available for combustion, which can reduce engine power output. This can be problematic for vehicles that require high power output, such as heavy-duty trucks.
- Can cause engine problems: EGR systems can malfunction or become clogged, which can lead to engine problems and reduced performance. Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the EGR system functions correctly.
In conclusion, while diesel exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) has many advantages, such as reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency and engine performance, it also has some drawbacks, including increased particulate matter emissions, increased engine complexity, reduced engine power output, and potential engine problems. The benefits of EGR systems should be weighed against their drawbacks to determine their suitability for specific diesel engine applications.




